Xiao Xiao
- 30
- 3
Thread moved from the technical forums, so no Homework Template is shown.
Summary:: The image shows two circuits, in the first one, using Nodal Analysis we find that V1=4.8V, but in the second circuit V1=10 because using KCL - 10+V1=0. I understand what happened in the first circuit, but I don't understand what happened in the second one, they look the same to me except for the existence of a supernode in the second one, which I don't think it should affect it in that way?
Not sure if this is the right forum to post in but this is not HW help since I already know the answer.
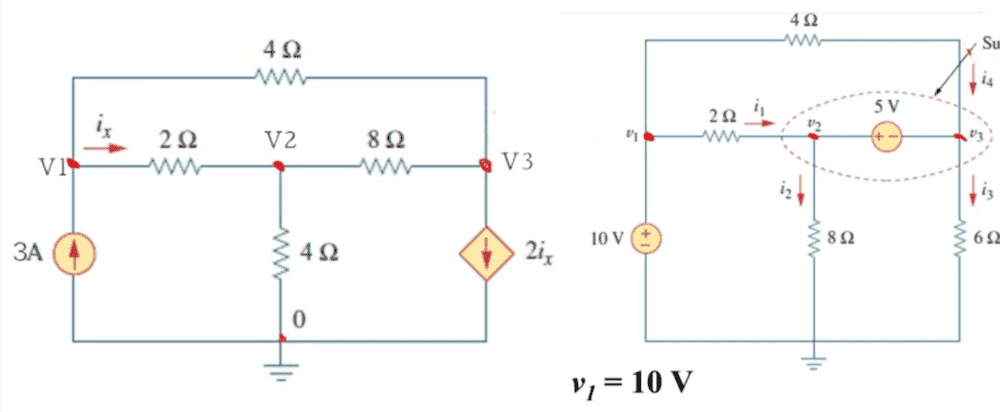
If I apply nodal analysis on the second circuit shouldn't I get a different result for V1?
Not sure if this is the right forum to post in but this is not HW help since I already know the answer.
If I apply nodal analysis on the second circuit shouldn't I get a different result for V1?