- #1
pebbles3
- 9
- 0
Homework Statement
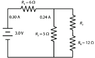
I'm supposed to find the missing resistances, currents, and voltages from the first picture (attached)
Homework Equations
v = IR
R = V/I
I=V/R
The Attempt at a Solution
My attempt is in the second attached picture. I'm completely lost on what to do for R3. Would R3 and R4 have the same voltage? I'd really appreciate some help with this.