- #1
slft
- 12
- 0
Homework Statement
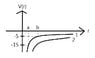
I understand the concept of negative potential energy value because it's chosen to be 0 at infinity. So considering two positive charges, as separation r increases, the potential energy V decreases.
When there's one positive and negative charge, as r increases, V increases. So from the graph, curve one, the potential energy at b is larger than at a (less negative), which makes sense to me. But I'm confused when comparing curve 1 and 2, where curve 2 involves larger charges, some multiple of curve 1. If there are larger charges, the potential energy in curve 2 larger (less negative) than that in curve 1. For example, for the potential energy at b, shouldn't the potential energy in curve 2 larger than -5? Can we compare it directly like we do for the same curve? or do we have to look at the magnitude of the negative value? but if so, how come we can compare directly the potential energy in the same curve with the value on the graph, while we can't compare different curve directly?