eyeweyew
- 35
- 6
- TL;DR Summary
- Electric potential at a point equation for circuit and net charge
I reviewed some of the fundamental physics and I looked back at the equation for Electric potential at a point p:
$$V(p) = k \sum_{i} {\frac {q_i} {r_i}}$$
where
- p is the point at which the potential is evaluated;
- ri is the distance between point p and point i at which there is a nonzero charge;
- qi is the charge at point i
and I still find it's kind of contradicting with the simple circuit model such as the one below. Both point a and point b should be neutral with no net charge so their electric field is 0 and the voltage is flat on the graph according to Gauss law. I understand the electric potential of point b is ε higher than that of point a (i.e. V(b)-V(a)=ε) means it takes ε work to move a +1 test charge from point a to point b along the circuit.
But according to Electric potential formula at a point, should that also imply there are higher positive net charge concentration around point b than point a so how can they both neutral with no net charge? Does that mean the equation for Electric potential at a point does not apply in a circuit model but if so, why?
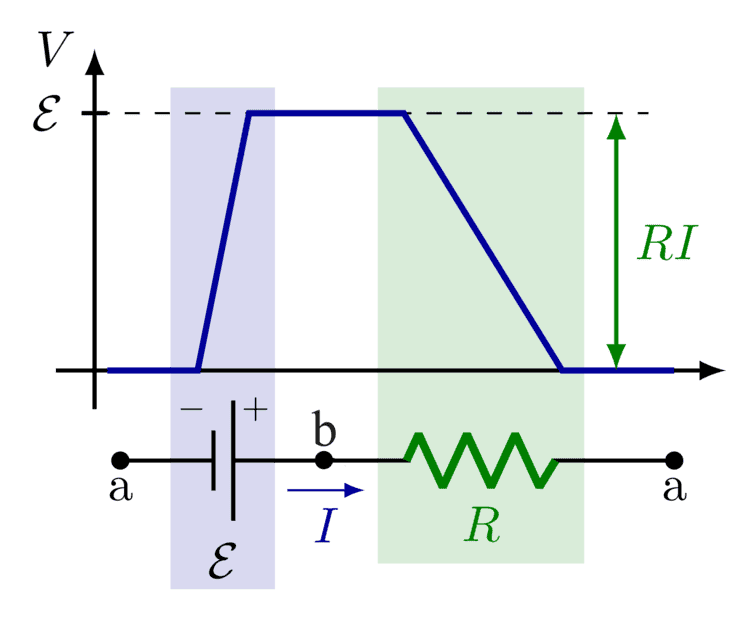
image reference: https://tikz.net/electric_circuit_voltage_plots/
$$V(p) = k \sum_{i} {\frac {q_i} {r_i}}$$
where
- p is the point at which the potential is evaluated;
- ri is the distance between point p and point i at which there is a nonzero charge;
- qi is the charge at point i
and I still find it's kind of contradicting with the simple circuit model such as the one below. Both point a and point b should be neutral with no net charge so their electric field is 0 and the voltage is flat on the graph according to Gauss law. I understand the electric potential of point b is ε higher than that of point a (i.e. V(b)-V(a)=ε) means it takes ε work to move a +1 test charge from point a to point b along the circuit.
But according to Electric potential formula at a point, should that also imply there are higher positive net charge concentration around point b than point a so how can they both neutral with no net charge? Does that mean the equation for Electric potential at a point does not apply in a circuit model but if so, why?
image reference: https://tikz.net/electric_circuit_voltage_plots/
Last edited: