- #1
Vibhor
- 971
- 40
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
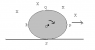
O is the center of the disk
Part a) The emf induced across PS can be found by thinking as if a rod PS is rotating and translating .
The component of velocity of rod perpendicular to its length is vsin45° = v/√2 . The length PS = √2R . Hence emf induced would be B(v/√2)(√2R) = BvR.
Is that correct ?
Thanks
Attachments
Last edited:
 til tomorrow)
til tomorrow)