- #1
greypilgrim
- 547
- 38
Hi.
I found following exercise in a high school textbook:
"Compute the entropy change in following process:"
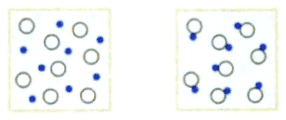
The solution is
"The number of particles decreases from ##N_1## to ##N_2=N_1/2##. Hence the entropy decreases by
$$\Delta S=-k\cdot N_1\cdot \ln{2}\enspace ."$$
I can't quite follow the argument here. Assuming the particles in each picture are non-interacting and have the same number of microstates ##\Omega##, I get
$$S_1=N_1\cdot k\cdot \ln{\Omega}$$
$$S_2=N_2\cdot k\cdot \ln{\Omega}=\frac{N_1}{2}\cdot k\cdot \ln{\Omega}=\frac{S_1}{2}$$
from which I can see that the entropy decreases, but cannot compute the difference since I don't know ##\Omega##.
I found following exercise in a high school textbook:
"Compute the entropy change in following process:"
The solution is
"The number of particles decreases from ##N_1## to ##N_2=N_1/2##. Hence the entropy decreases by
$$\Delta S=-k\cdot N_1\cdot \ln{2}\enspace ."$$
I can't quite follow the argument here. Assuming the particles in each picture are non-interacting and have the same number of microstates ##\Omega##, I get
$$S_1=N_1\cdot k\cdot \ln{\Omega}$$
$$S_2=N_2\cdot k\cdot \ln{\Omega}=\frac{N_1}{2}\cdot k\cdot \ln{\Omega}=\frac{S_1}{2}$$
from which I can see that the entropy decreases, but cannot compute the difference since I don't know ##\Omega##.