slam
- 1
- 0
- Homework Statement
- Neutron diffusion in nuclear reactor - deriving the equation of the slowing of the neutrons in momentum space and of their struggle to pass through the 238U resonance region without getting absorbed.
- Relevant Equations
- Boltzmann eq., Neutron transport eq., Neutron diffusion eq.
I am trying to solve a problem from Thorne and Blandford: Modern classical physics, chapter 3, problem 21: Neutron diffusion in nuclear reactor.

I am struggling with how the equation, from which this should be calculated, should look like. I watched some videos where they did the derivation a such equation, however I don't know how to simplify it to fit my conditions. I think it should look roughly like this:
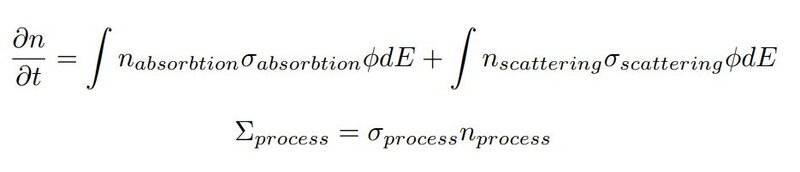
I'm not sure if there are supposed to be more terms or by what factors they should be multiplied, so is it somehow correct and I just need to add correct normalization, or am I completely wrong?
If someone could explain to me how to precisely create the equation from which I could get the desired relations, I would really appreciate it. Thanks!
I am struggling with how the equation, from which this should be calculated, should look like. I watched some videos where they did the derivation a such equation, however I don't know how to simplify it to fit my conditions. I think it should look roughly like this:
I'm not sure if there are supposed to be more terms or by what factors they should be multiplied, so is it somehow correct and I just need to add correct normalization, or am I completely wrong?
If someone could explain to me how to precisely create the equation from which I could get the desired relations, I would really appreciate it. Thanks!