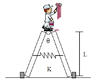
- #1
Hernaner28
- 263
- 0
Homework Statement
I have that situation in which I'm told that the blocks each support a maximum force of 20N. Neglect the natural state of the spring. And I'm asked to find the MINIMUM value of the spring constant K for the man to be secure with an angle [tex] \displaystyle \theta =30{}^\text{o}[/tex].
This is known data:
[tex] \displaystyle \begin{align}
& m=70,0kg \\
& L=3,00m \\
\end{align}[/tex]
Homework Equations
Newton and Torque.
The Attempt at a Solution
What I did first was to work with half of the problem (only one side of the ladder) and worked with the half of the man weight as well.
So I wrote:
NEWTON:
[tex] \displaystyle \sum{{{F}_{y}}=\frac{-mg}{2}+{{N}_{1}}\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\frac{mg}{2}}[/tex]
Where N1 is the vertical normal.
The equation in axis x is irrelevant.
TORQUE:
[tex] \displaystyle \sum{\tau }={{N}_{2}}\cos 15{}^\text{o}H+F\cos 15{}^\text{o}\frac{H}{2}-{{N}_{1}}\sin 15H=0[/tex]
Where N2 is the horizontal normal caused by the block, H is the distance of the ladder:
[tex] \displaystyle H=\frac{L}{\cos 15{}^\text{o}}[/tex]
and F is the force done by the spring. So:
[tex] \displaystyle F=kx[/tex]
where x is:
[tex] \displaystyle x=\frac{H}{2}\sin 15{}^\text{o}[/tex]
Solving for K I get the minimum value should be 360 N/m but that's not the correct option. The one marked as correct is 179N/m. What was my mistake?
Thanks!