- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
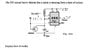
In summary, the conversation is about a problem with an attached homework question involving a 555 timer. The person is unsure about the appropriate answer and is seeking suggestions. They mention some properties of the 555 timer and how it behaves with different inputs. They also mention not knowing what the transistor across the timing capacitor would do. The conversation ends with a recommendation to do a search on "555 missing pulse" and to understand the block diagram of the 555 timer.
Physics news on Phys.org
- #2
gneill
Mentor
- 20,989
- 2,934
I'm not sure what your appropriate attempt at a solution is 
- #3
maherelharake
- 261
- 0
Haha yeah sorry it seems as if I didn't even think about it.
Well I know that 555's have properties such as:
low trigger input leads to high output
high trigger input leads to low output
it outputs a square wave
if the trigger isn't a max/min then there is no output
Not sure if these ideas are leading me up the correct path.
Well I know that 555's have properties such as:
low trigger input leads to high output
high trigger input leads to low output
it outputs a square wave
if the trigger isn't a max/min then there is no output
Not sure if these ideas are leading me up the correct path.
- #4
gneill
Mentor
- 20,989
- 2,934
You need to figure out what the state of the 555 would be (that is, the output) if there were no input signal. Then what happens when a negative going input edge occurs (say just one negative going pulse). The internal block diagram for the 555 might help.
What will be the result of repeated input pulses? What's the transistor across the timing capacitor going to do?
What will be the result of repeated input pulses? What's the transistor across the timing capacitor going to do?
- #5
maherelharake
- 261
- 0
Well based off my previous statements, would no input signal lead to a high output?
I don't know what would happen if an input edge occurs.
Wouldn't repeated input pulses just give repeated outputs?
I also don't know what the transistor would do
I'm not that great at this stuff
I don't know what would happen if an input edge occurs.
Wouldn't repeated input pulses just give repeated outputs?
I also don't know what the transistor would do
I'm not that great at this stuff
- #6
gneill
Mentor
- 20,989
- 2,934
Do a google search on "555 missing pulse". You should turn up a circuit operation description. But you should really try to understand the block diagram of the 555 so that the operation is clear. The 555 is composed of some pretty simple functions that are just wired together in a clever way, and allow the 555 to behave in some very useful ways with just small changes in external wiring.
FAQ: Explaining How 555 Circuit works
How does a 555 circuit work?
The 555 circuit is a type of integrated circuit (IC) that is commonly used in electronic devices. It is a timer circuit that can generate precise square wave signals with a variety of frequencies and duty cycles. It consists of three main components: a voltage divider network, a comparator, and a flip-flop. The voltage divider network sets the trigger and threshold levels, while the comparator compares the input voltage with these levels. The flip-flop then generates the output signal based on the comparison result.
What is the purpose of the 555 timer circuit?
The 555 timer circuit can be used for a variety of purposes, such as generating clock signals, creating tone generators, and controlling the timing of electronic systems. It is also commonly used in applications that require precise timing, such as in electronic circuits, devices, and systems.
How is the output frequency determined in a 555 circuit?
The output frequency of a 555 circuit is determined by the values of the external resistors and capacitors connected to it. The frequency can be calculated using the equation: f = 1.44 / (R1 + 2R2)C, where R1 and R2 are the external resistors and C is the external capacitor. By changing these values, the output frequency can be adjusted to meet the specific requirements of the application.
What is the difference between astable and monostable operation in a 555 circuit?
In astable operation, the 555 circuit continuously generates a square wave signal with a specific frequency and duty cycle. This mode is commonly used in applications that require a continuous output signal, such as in LED flashers or tone generators. In monostable operation, the 555 circuit generates a single pulse of a specific duration in response to a trigger signal. This mode is commonly used in applications that require a one-shot pulse, such as in electronic switches or timers.
Can the 555 timer circuit be used with different power supply voltages?
Yes, the 555 timer circuit can operate with a wide range of power supply voltages, typically from 4.5V to 18V. However, the output voltage level will depend on the power supply voltage and the load connected to the output pin. It is important to note that the maximum power supply voltage should not exceed 18V, as it could damage the IC.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 460
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 926
- Replies
- 10
- Views
- 951
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 545
- Replies
- 32
- Views
- 5K
- Replies
- 15
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 6K
- Replies
- 6
- Views
- 457
- Replies
- 16
- Views
- 523
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 755
Share: