- #1
Hugofung
- 2
- 0
Such as the figure
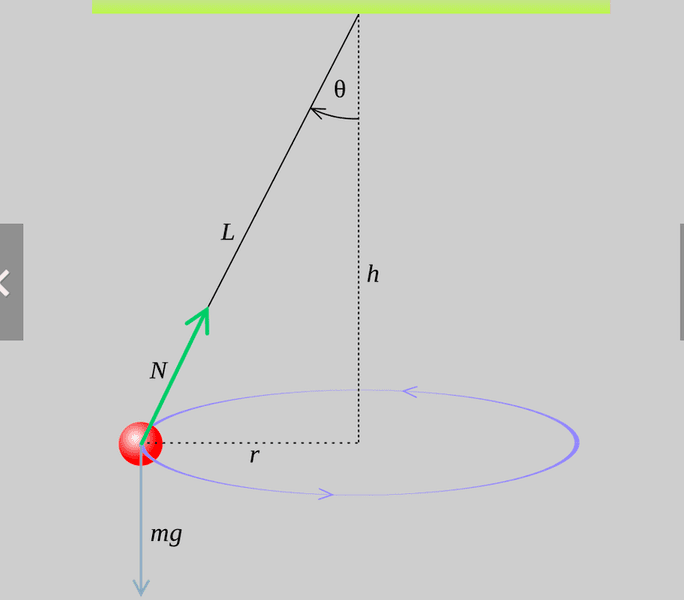
Why the string could not be horizontal when the rubber bungis moving in a horizontal circle?
Only moving at conical pendulum?
By the way, if tension is equal to weight(W), have any conclusion?
Why the string could not be horizontal when the rubber bungis moving in a horizontal circle?
Only moving at conical pendulum?
By the way, if tension is equal to weight(W), have any conclusion?