- #1
Lambda96
- 229
- 75
- Homework Statement
- Show that the vector ##W_n## is orthogonal to all vectors ##w_j##
- Relevant Equations
- none
Hi,
unfortunately, I have problems with the task c

I used the tip with the Laplace evolution theorem and rewrote the determinant to calculate ##W_n##. Then I simply formed the scalar product ##W_1 W_n## and here I get now no further.
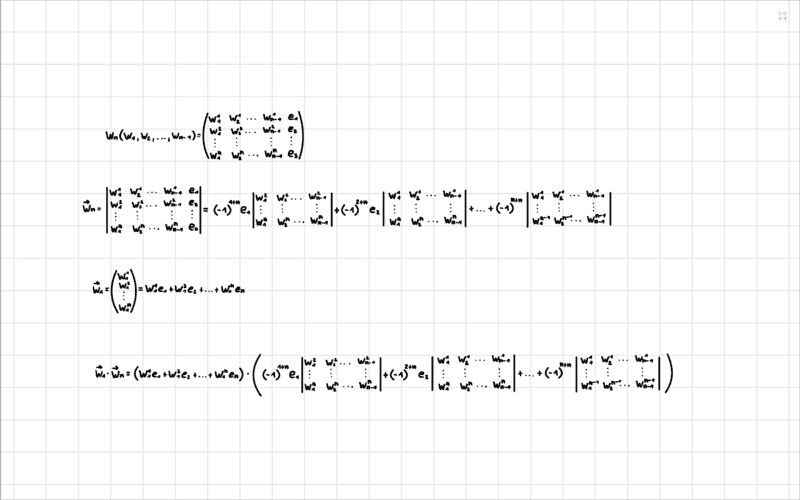
unfortunately, I have problems with the task c
I used the tip with the Laplace evolution theorem and rewrote the determinant to calculate ##W_n##. Then I simply formed the scalar product ##W_1 W_n## and here I get now no further.