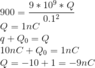- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
In summary, the conversation is about a homework problem involving the equation E= kQ/r^2. The answer to the problem is "A", but the student is unsure and asks for confirmation. The responder reminds the student that the forum is not for stamp-approvals and encourages them to trust their own answer. However, the student makes a mistake in their calculation of Q, but the answer is still correct. The responder reminds the student to pay more attention to units in equations.
Physics news on Phys.org
- #2
BvU
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 16,118
- 4,875
Hello Fatima,
PF is not intended for stamp-approvals. If you convince yourself that -9 nC is the right answer, then that IS your answer for this exercise !
And why shouldn't it be the right answer ?
PF is not intended for stamp-approvals. If you convince yourself that -9 nC is the right answer, then that IS your answer for this exercise !
And why shouldn't it be the right answer ?
- #3
BvU
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 16,118
- 4,875
Yeah, well...
- #4
Fatima Hasan
- 319
- 14
I was not pretty sure. Just wanted to confirm my answer. Sorry for multiple questions but my exam is after hours. I wish I have not broken the forum rules. ThanksBvU said:Hello Fatima,
PF is not intended for stamp-approvals. If you convince yourself that -9 nC is the right answer, then that IS your answer for this exercise !
And why shouldn't it be the right answer ?
Last edited:
- #5
BvU
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 16,118
- 4,875
Best of luck for your test! 
- #6
ehild
Homework Helper
- 15,542
- 1,917
You wrote that Q=1 nC and then that Q=-10+1 =-9 nC. These are wrong, although the answer "A" is correct. Pay more attention!Fatima Hasan said:Homework Statement
View attachment 223911
Homework Equations
##E=\frac{kQ}{r^2}##
The Attempt at a Solution
View attachment 223912
The answer is "A".Right ?
- #7
Fatima Hasan
- 319
- 14
##Q_0=-10+1=-9nC##ehild said:You wrote that Q=1 nC and then that Q=-10+1 =-9 nC. These are wrong, although the answer "A" is correct. Pay more attention!
- #8
ehild
Homework Helper
- 15,542
- 1,917
-10+1 is not -9 nC . Write out the units at both sides of an equation.Fatima Hasan said:##Q_0=-10+1=-9nC##
FAQ: Find the charge on the outer surface
What is meant by "charge on the outer surface"?
The charge on the outer surface refers to the net electric charge that is present on the surface of a conductor or object.
How do you find the charge on the outer surface?
The charge on the outer surface can be found by using the Gauss's Law, which states that the net electric flux through a closed surface is equal to the enclosed charge divided by the permittivity of free space.
What factors affect the charge on the outer surface?
The charge on the outer surface is affected by the amount of charge enclosed within the surface, the size and shape of the surface, and the permittivity of the surrounding medium.
Can the charge on the outer surface be negative?
Yes, the charge on the outer surface can be negative if the net charge enclosed within the surface is negative.
Why is it important to find the charge on the outer surface?
Finding the charge on the outer surface is important in understanding the behavior of electric fields and their effects on conductors and objects. It also helps in determining the electric potential and capacitance of a system.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 944
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 19
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 35
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 14
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 15
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 3K
Share: