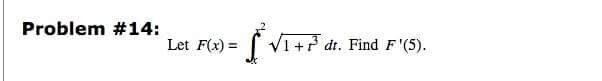Umar
- 36
- 0
I know it seems pretty self explanatory, but I've tried to do this question and I've apparently gotten the wrong answer twice.
View attachment 6169
If anyone can give me a clear solution to the problem, that would be greatly aooreciated. I initially tried to follow a video I saw online, but I think there is something different I need to do considering the bounds. Maybe splitting the integral?
View attachment 6169
If anyone can give me a clear solution to the problem, that would be greatly aooreciated. I initially tried to follow a video I saw online, but I think there is something different I need to do considering the bounds. Maybe splitting the integral?