- #1
physicsnerd26
- 20
- 0
I feel terrible for even having to ask this. I'm doing A2 at the moment, and we've gone through these sorts of lessons ever since my early AS days. I'm trying to review my notes cos exams are coming soon and I did some questions, and I'm apparently doing them wrong with what the answers are showing me at the back of the book.
Can anybody explain it to me? I'm talking about the kind of graph that goes from negative to positive.
Here's an example of a graph I'm talking about I found on the internet:
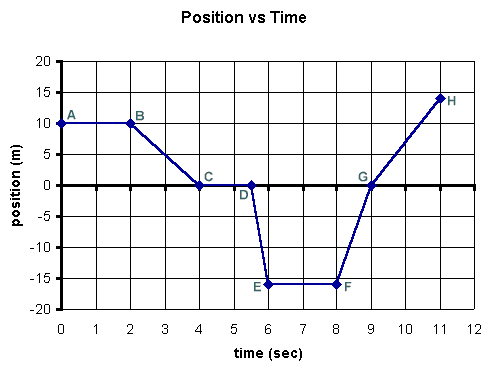
What I do is technically
A to B would be -> 10 x 2 = 20m
B to C would be -> (10 x 2)/2 = 10m
C to D would be 0
D to E would be - > (0.5 x -15)/2 = -3.75m, but it's distance so it's 3.75m
E to F would be 0
F to G would be -> (15 x 1)/2 =7.5m
G to H would be -> (2 x 15)/2 = 15m
so overall, I just add them all up so, 20+10+3.75+7.5+15 = 56.25m
Have I been doing it completely wrong?
Can anybody explain it to me? I'm talking about the kind of graph that goes from negative to positive.
Here's an example of a graph I'm talking about I found on the internet:
What I do is technically
A to B would be -> 10 x 2 = 20m
B to C would be -> (10 x 2)/2 = 10m
C to D would be 0
D to E would be - > (0.5 x -15)/2 = -3.75m, but it's distance so it's 3.75m
E to F would be 0
F to G would be -> (15 x 1)/2 =7.5m
G to H would be -> (2 x 15)/2 = 15m
so overall, I just add them all up so, 20+10+3.75+7.5+15 = 56.25m
Have I been doing it completely wrong?