- #1
charlies1902
- 162
- 0
Homework Statement
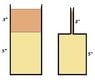
I attached the problem.
Please check my work.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
Density of oil=.92*1000=920 kg/m3
Density of vinegar=1010 kg/m3
Height of oil=3*.0254=.0762 m
Heigh of water=.127 m
a) Gage pressure at bottom=(920)(9.81)(.0762)+(1010)(9.81)(.127)=1946 Pa
b) The words "side of the bottle" kinda threw me off. It made me think they were referring to outside the bottle. I assumed it was still inside the bottle. I guess the word "side" was intended to throw you off as the horizontal direction does not matter.
Gage pressure between oil&vinegar=(920)(9.81)(.0762)=688 Pa
c) I'm going to guess that shaking the bottle so that the two are thoroughly mixed will still end up having the same pressure as part a) 1946 Pa? I don't know how to explain that, but it seems logical to me. If that's the answer, can someone explain why it is?