- #1
Karol
- 1,380
- 22
Homework Statement
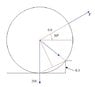
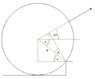
The cylinder with mass 200[kg] and radius 0.8[m] tries to climb a 0.3[m] high edge with a force F exerted at an angle of 300. what's the force and what's the minimum force for the cylinder to climb
Homework Equations
Moments: F1L1=F2L2
The Attempt at a Solution
The weight balances the the force, i made moments around the edge and got a true answer F=1670[N], but i don't understand the second question, about the minimum force, and it's about 766[N]