- #1
nelson_qna
- 3
- 0
Hi Everyone.
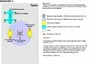
I've been trying to build an electrical motor and would like know the method to actually calculate the forces exerted on several parts in the motor according to Newton's laws. I've attached some pictures and drawings of the motor I'm trying to build. There are two scenarios that I've considered. Scenario 1 (Please see drawings Scenario 1) & Scenario 2 (Please see drawing Scenario 2)
Question 1 - "According to Drawing in Scenario 1"
Is my interpretation of all the forces involved in the motor correct according to Newton's Law? (Dismissing Friction Of Course)
Question 2 - "According to Drawing in Scenario 2"
In scenario 2 is all the forces involved in the drawing of scenario 2 correct and does it violets Newton's laws?
It feels wrong as 10N is acting on the 4 bolts in the + direction and 5N is acting on the pin (Q) in the - Direction. This 2 forces should be equal according to Newton's laws. If not there will be a nett force of -5N acting on the table. I just can't see how 10N of force is transferred from the permanent magnets to point Q where the bearing pivots.
Please Explain Thank You.
I've been trying to build an electrical motor and would like know the method to actually calculate the forces exerted on several parts in the motor according to Newton's laws. I've attached some pictures and drawings of the motor I'm trying to build. There are two scenarios that I've considered. Scenario 1 (Please see drawings Scenario 1) & Scenario 2 (Please see drawing Scenario 2)
Question 1 - "According to Drawing in Scenario 1"
Is my interpretation of all the forces involved in the motor correct according to Newton's Law? (Dismissing Friction Of Course)
Question 2 - "According to Drawing in Scenario 2"
In scenario 2 is all the forces involved in the drawing of scenario 2 correct and does it violets Newton's laws?
It feels wrong as 10N is acting on the 4 bolts in the + direction and 5N is acting on the pin (Q) in the - Direction. This 2 forces should be equal according to Newton's laws. If not there will be a nett force of -5N acting on the table. I just can't see how 10N of force is transferred from the permanent magnets to point Q where the bearing pivots.
Please Explain Thank You.