StoyanNikolov
- 50
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Forces on rotating disk object
Forces on rotating disk object
Hi. Is it convenient to ask following question.
Suppose we have solid circular object and 5 different moments
like in the picture:
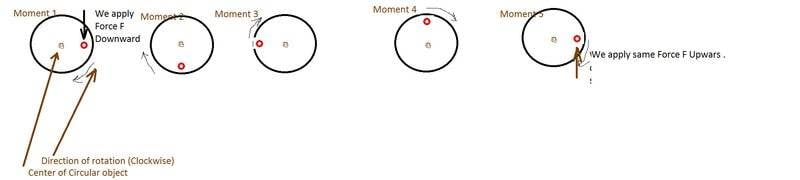 In moment 1 we apply force (downwars direction) so as to start rotating the object around center of
In moment 1 we apply force (downwars direction) so as to start rotating the object around center of
the mass (green dot) , Only rotational motion.
In moment 2-moment 4 the object is rotating around the green dot at the center of the object
(center of the mass), while the center of the mass is not moving.
In moment5 we apply upward same force as force applied in moment1 but in upward direction.
Will the center of mass of the circular object start moving in some direction.
In moment 5
Will there be also translational (not only rotational) motion ?
Will the center of the disk start going in some direction?
Thank you.
Hi. Is it convenient to ask following question.
Suppose we have solid circular object and 5 different moments
like in the picture:
the mass (green dot) , Only rotational motion.
In moment 2-moment 4 the object is rotating around the green dot at the center of the object
(center of the mass), while the center of the mass is not moving.
In moment5 we apply upward same force as force applied in moment1 but in upward direction.
Will the center of mass of the circular object start moving in some direction.
In moment 5
Will there be also translational (not only rotational) motion ?
Will the center of the disk start going in some direction?
Thank you.
