garryA
- 11
- 3
- TL;DR Summary
- Transmission coefficient vs Reflection coefficient of FSS radome
So I was reading about frequency selective surface radome, basically this is the kind of cover over the antenna which allow a certain frequency wave to pass through and reflect wave at any other frequencies.
What I don't understand is the reflection vs transmission coefficient chart.
So as I understand it.
The transmission coefficient is a measure of how much of an electromagnetic wave passes through a surface
The reflection coefficient is a a measure of how much of an electromagnetic wave reflected when it hit a surface, The reflection coefficient determines the ratio of the reflected wave amplitude to the incident wave amplitude.
So logically, wouldn't the two value always opposite?
Let me give a practical example:
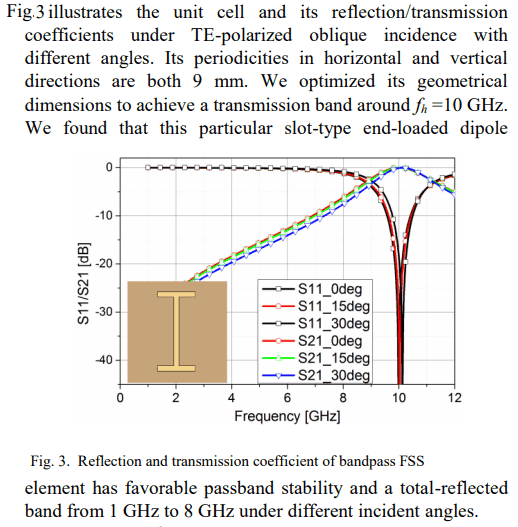
below, the band pass frequency is 10Ghz, so the transmission coefficient is 0 dB while the reflection coefficient is extremely small (like -40 dB). That make total sense because if it reflect nothing then most energy can pass through the layer
But take for example at 6Ghz, the reflection coefficient is at 0 dB, meaning it reflect everything, so how come the transmission coefficient is not at -40 dB?.
Shouldn't the shape of the two curve for reflection/transmission coefficient completely reverse each other?
What I don't understand is the reflection vs transmission coefficient chart.
So as I understand it.
The transmission coefficient is a measure of how much of an electromagnetic wave passes through a surface
The reflection coefficient is a a measure of how much of an electromagnetic wave reflected when it hit a surface, The reflection coefficient determines the ratio of the reflected wave amplitude to the incident wave amplitude.
So logically, wouldn't the two value always opposite?
Let me give a practical example:
below, the band pass frequency is 10Ghz, so the transmission coefficient is 0 dB while the reflection coefficient is extremely small (like -40 dB). That make total sense because if it reflect nothing then most energy can pass through the layer
But take for example at 6Ghz, the reflection coefficient is at 0 dB, meaning it reflect everything, so how come the transmission coefficient is not at -40 dB?.
Shouldn't the shape of the two curve for reflection/transmission coefficient completely reverse each other?
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: