orangephysik
- 11
- 1
- Homework Statement
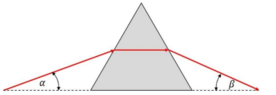
- A prism made from glass with a refractive index of n has the form of an equilateral triangle. A light ray is directed to one side of the prism with has an angle of α = 24.5° to the ground. You observe that the light ray inside the prism travels parallel to the ground.
a) Calculate the refractive index n.
b) Find the angle at which the ray leaves the prism and find β.
- Relevant Equations
- Snell's law: n_1*sin(m) = n_2 * sin(n)
All angles inside of a triangle sum up to 180°
Properties of equilateral triangles and isosceles triangles
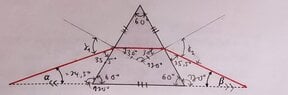
Hi, I've attached the photo of the diagram, a photo of my drawings on the diagram.
for a): Since the prism is an equalateral triangle, all angles inside the prism is 60°. This means the angle adjacent to α is 180° - 60° = 120°, which means the last angle is 180° - 24.5° - 120° = 35.5°. The smaller triangle within the prism is an isosceles triangle, and by intuition the angle in the middle is 120° and the two angles on the sides are 30°.
Now with snell's law, n_vacuum * sin(γ_1) = n * sin(30°) and γ_1 = 90° - 35.5° 54.5°.
Plugging these values in, I got n = 1.628.
Is this correct? I thought the solution is plausible since the refractive index of a glass is usually around 1.5.
and for b) I just used the equation from snell's law again, n * sin(30°) = n_vacuum * sin(γ_2).
for a): Since the prism is an equalateral triangle, all angles inside the prism is 60°. This means the angle adjacent to α is 180° - 60° = 120°, which means the last angle is 180° - 24.5° - 120° = 35.5°. The smaller triangle within the prism is an isosceles triangle, and by intuition the angle in the middle is 120° and the two angles on the sides are 30°.
Now with snell's law, n_vacuum * sin(γ_1) = n * sin(30°) and γ_1 = 90° - 35.5° 54.5°.
Plugging these values in, I got n = 1.628.
Is this correct? I thought the solution is plausible since the refractive index of a glass is usually around 1.5.
and for b) I just used the equation from snell's law again, n * sin(30°) = n_vacuum * sin(γ_2).