- #1
dom_quixote
- 50
- 9
The gravitational mapping of the GROCE satellite projects to the left - at sea level - a rough outline formed by the Nordic countries, Finland and part of Russia.
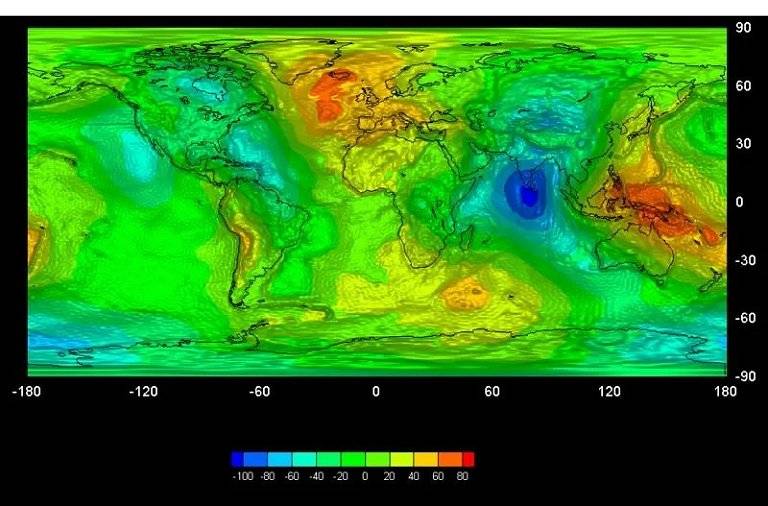
The same goes for Australia.
The same goes for Australia.