johnlpmark
- 17
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
- Why does the gyroscopic precession of a spin-stabilized bullet cause drift in the same direction as the spin?
Hi!
I am trying to understand the physics behind the gyroscopic phenomenon called spin drift. Spin drift occurs to bullets that are spin-stabilized over the course of their flight.
Spin drift starts with an induced rotation in a spin stabilized bullet. As a bullet flies through the air, gravity causes the apparent direction of the incoming air to change as the bullet flies in a parabolic trajectory. The bullet tips into the direction of the incoming air (called weather-vaning). From the perspective of the bullet, this is a forward rotation.
Gyroscopic precession occurs when the bullet translates this forward rotation 90 degrees due to gyroscopic precession. Thereby, the bullet translates some of the downward tipping into sideways tipping. When tipped sideways, lift forces cause the bullet to change the direction of travel into whatever direction the bullet is pointed. That is, the reverse of weather-vaning occurs: instead of drag causing a change in orientation, lift causes a change in travel vector.
In sum, spin drift causes a bullet to always turn to the right and go right when fired with a right or clockwise (from the perspective of the shooter) spin. And a bullet left for a left twist. "Precession 90 degrees in the direction of spin. The gyroscopic force translates that nose-up, tail-down torque on the fast-spinning bullet into a nose-right yaw on the bullet because most rifling is to the right (clockwise ) from the shooter’s perspective." As far as I can tell, spin drift should occur to the opposite direction of spin, but that is not the case.My question is not on why spin drift or gyroscopic precession occurs, but rather why it occurs to the right or left. The problem I have is that spin drift occurs in the same direction of spin. That is, right spinning bullet (a clockwise spinning bullet when viewed from the rear) turns right. This is well-attested empirically. However, whenever I view diagrams and explanations, or experiment with a gyroscope myself, a right spin should force a forward rotation to induce a left turn.
One possible explanation is that there are two axes of spin. The first axis is the center of mass of the bullet itself. The second and larger axis is the axis of travel. When bullets travel, they do so in a helix pattern, and not a straight line. If a right-spinning bullet creates a left-spinning helix, it could explain why spin drift occurs in the same direction as the spin. But I don't really know.
I've searched everywhere! Please help me understand. I am not a phyisist, and do not understand nor have any need for equations. This paper probably explains how it works, but I can't read it well enough to understand this one particular aspect. A Coning Theory of Bullet Motions | James A. Boatright | Revised: March 2018 . Also, if it is relevant, for bullets the center of pressure (COP) is always ahead of the center of gravity (COG).Thanks so much for your help!
Here are some pictures to help understand what I am talking about
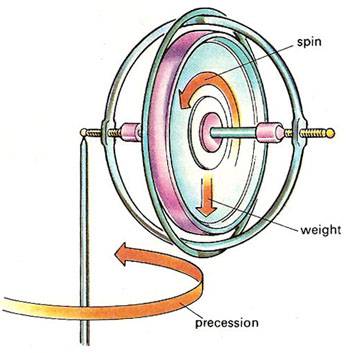
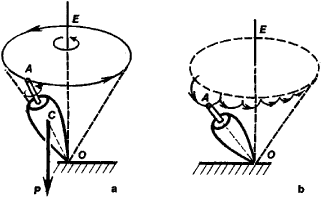
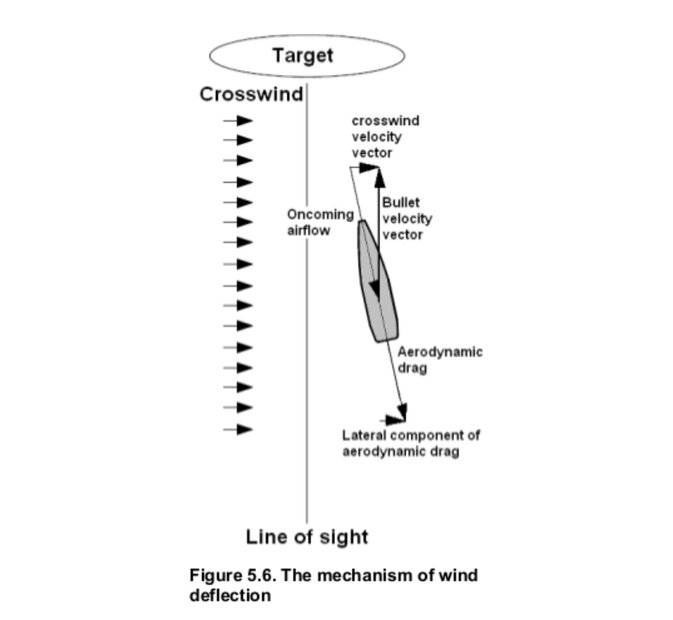
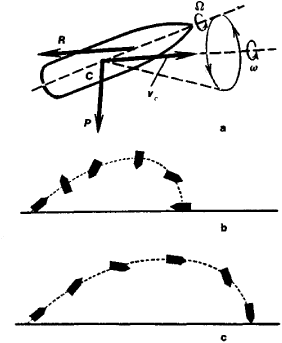
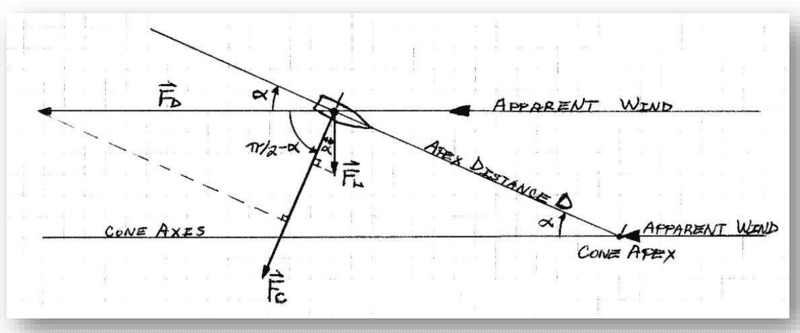
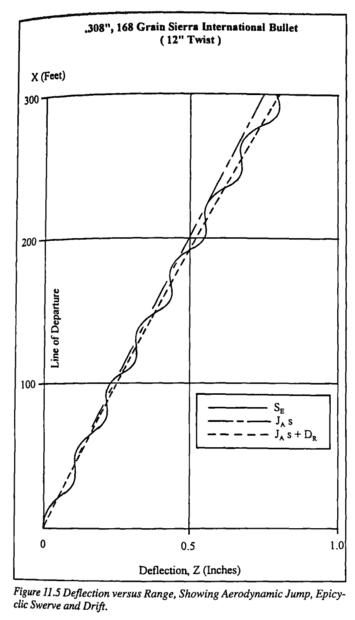
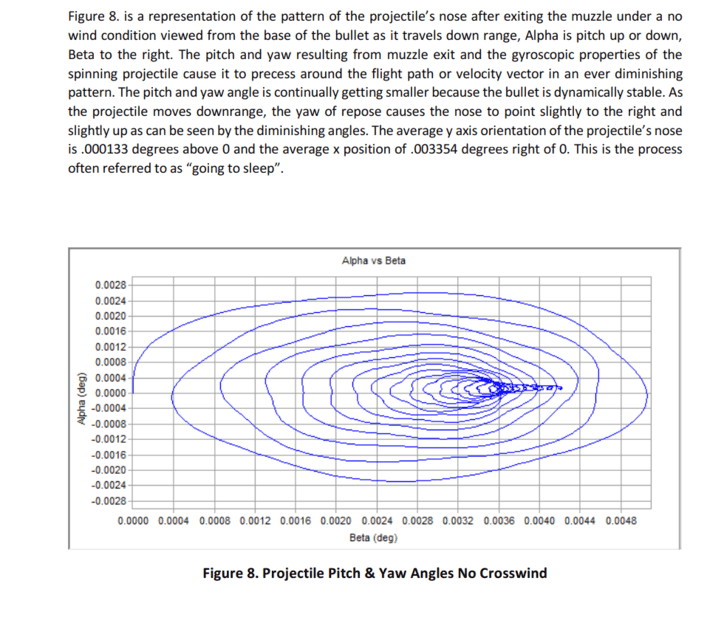
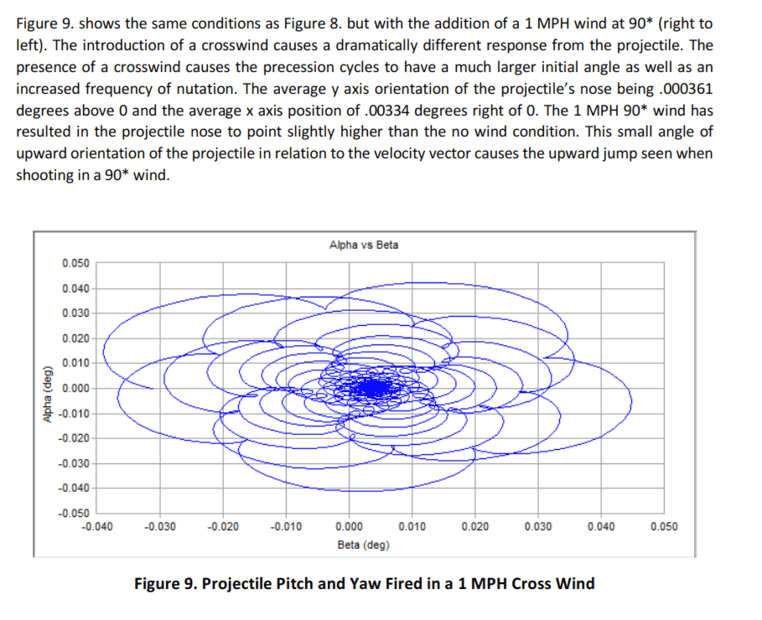
I am trying to understand the physics behind the gyroscopic phenomenon called spin drift. Spin drift occurs to bullets that are spin-stabilized over the course of their flight.
Spin drift starts with an induced rotation in a spin stabilized bullet. As a bullet flies through the air, gravity causes the apparent direction of the incoming air to change as the bullet flies in a parabolic trajectory. The bullet tips into the direction of the incoming air (called weather-vaning). From the perspective of the bullet, this is a forward rotation.
Gyroscopic precession occurs when the bullet translates this forward rotation 90 degrees due to gyroscopic precession. Thereby, the bullet translates some of the downward tipping into sideways tipping. When tipped sideways, lift forces cause the bullet to change the direction of travel into whatever direction the bullet is pointed. That is, the reverse of weather-vaning occurs: instead of drag causing a change in orientation, lift causes a change in travel vector.
In sum, spin drift causes a bullet to always turn to the right and go right when fired with a right or clockwise (from the perspective of the shooter) spin. And a bullet left for a left twist. "Precession 90 degrees in the direction of spin. The gyroscopic force translates that nose-up, tail-down torque on the fast-spinning bullet into a nose-right yaw on the bullet because most rifling is to the right (clockwise ) from the shooter’s perspective." As far as I can tell, spin drift should occur to the opposite direction of spin, but that is not the case.My question is not on why spin drift or gyroscopic precession occurs, but rather why it occurs to the right or left. The problem I have is that spin drift occurs in the same direction of spin. That is, right spinning bullet (a clockwise spinning bullet when viewed from the rear) turns right. This is well-attested empirically. However, whenever I view diagrams and explanations, or experiment with a gyroscope myself, a right spin should force a forward rotation to induce a left turn.
One possible explanation is that there are two axes of spin. The first axis is the center of mass of the bullet itself. The second and larger axis is the axis of travel. When bullets travel, they do so in a helix pattern, and not a straight line. If a right-spinning bullet creates a left-spinning helix, it could explain why spin drift occurs in the same direction as the spin. But I don't really know.
I've searched everywhere! Please help me understand. I am not a phyisist, and do not understand nor have any need for equations. This paper probably explains how it works, but I can't read it well enough to understand this one particular aspect. A Coning Theory of Bullet Motions | James A. Boatright | Revised: March 2018 . Also, if it is relevant, for bullets the center of pressure (COP) is always ahead of the center of gravity (COG).Thanks so much for your help!
Here are some pictures to help understand what I am talking about