- #1
FUT7CAP
- 2
- 0
Consider a toroidal coil of rectangular section of N turns, for every one of which circulates a stream I. The inner radius of the coil is a and b is the exterior and the height is h. The core of this coil is a material inhomogeneous in such a way that their magnetic permeability just depends on the angle theta in this way
[tex]\mu o=(1+k cos\theta)\mu[/tex]
vector magnetic field H ?
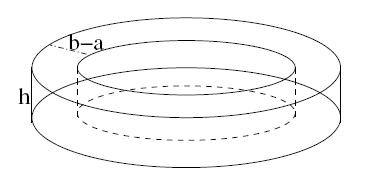
Please, can u solve this?? I can´t find the answer...
Thanks,
José
[tex]\mu o=(1+k cos\theta)\mu[/tex]
vector magnetic field H ?
Please, can u solve this?? I can´t find the answer...
Thanks,
José
Last edited: