- #1
Effect
- 13
- 0
In a demonstrational heat pump, according to figure 1, heat QC = Qin is taken from a "cold reservoir" that contains 10 liter mix of water and glycol. Heat QH = Qout is dissipated to a “hot reservoir” that contains 10 liters of water. QC is the heat that you normally get "for free" from a suitable reservoir and QH is useful heat that we normally use for heating. The compressor adds the work W that we pay for with the electric bill.
Figure 1. A heat pump with the most important parts drawn. Compressor, expansion valve, cold and hot reservoir.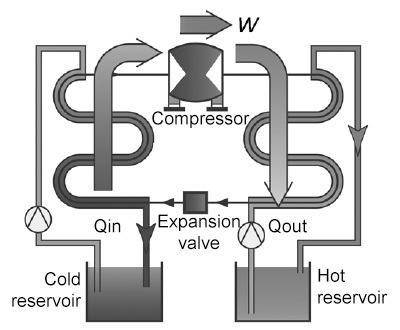
a) The temperature in the hot reservoir was increased with 25.8 °C in 1616 s. How big average power has been given to the hot reservoir?
b) The diagram in figure 2 shows how the temperature TH in the hot reservoir is varies with time t. The measurement started when the heat pump started.
Figure 2. The variation of temperature with time in the hot reservoir.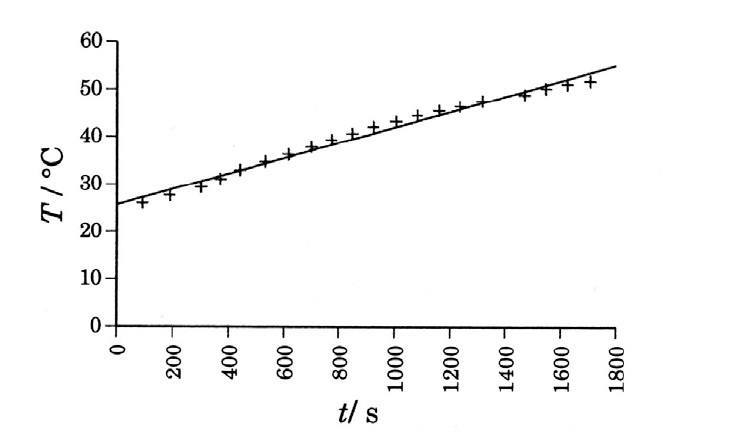
We fit a straight line to the measurement points with the least square method and get:
[tex]T_{H} = a \cdot t + b[/tex] where a = 0,0163 °C/s and b = 25,7 °C.
We assume that the power of the compressor is constantly 158 W during the time of measurement. Calculate the coefficient of performance COPHP for the heat pump when the temperature varies according to the above.
[tex]COP_{HP}(t)=\frac{Q_{H}}{W}=\frac{dQ_{H}(t)}{dt}/\frac{dW(t)}{dt}=\frac{P_{out}(t)}{P_{in}(t)}[/tex]
where Pout is the power that is transmitted to the hot reservoir and Pin is the electric power used by the compressor.
Hint:
[tex]P_{out}=\frac{dQ_{H}}{dt}=\frac{dQ_{H}}{dT}\cdot \frac{dT}{dt}=m\cdot c\cdot \frac{dT}{dt}[/tex]
So if we start with question a) to calculate P = Q/t we can use that Q=m*c*ΔT so for for the 10 liters of water in the hot reservoir we get P=10*4186*25.8/1616=668 W.
However it says the answer for a) is 667 W. Any idea why the difference?
For question b) we have Vf = Pout / Pin where Pout = m*c*dT/dt
dT/dt = a*t^-1 so Vf = m*c*a*t^-1 / Pin = 10*4186*0.0163 / 158 = 4.3
Here the number is correct but I wonder about something about the units. The variable a is said to have unit °C/s so when deriving with respect to time we should get °C/s^2 ? But in order for the answer to be correct the unit should rather be K/s in order for COP to be unitless? Please help how can this be cleared up?