- #1
Zandabyte
- 2
- 0
This is what I was able to get from the problem but it is clearly wrong and I have no idea what the right way to go about this would be. Thank you in advance for your help.
1/3:
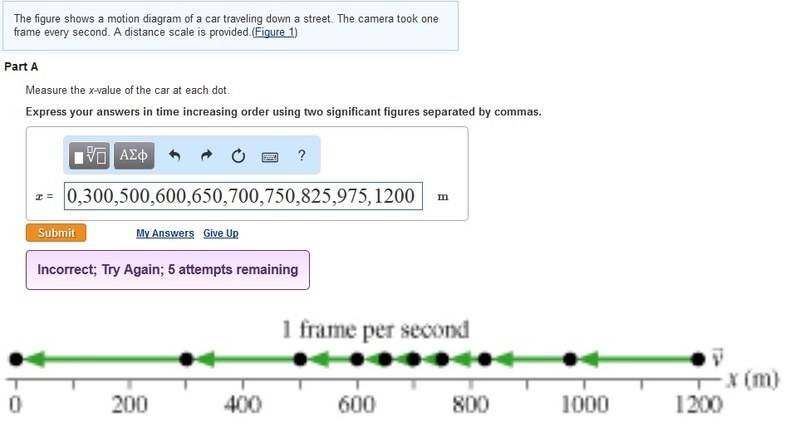
Homework Equations
: None available for this type of problem.[/B]1/3: