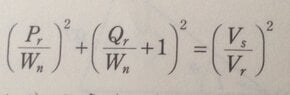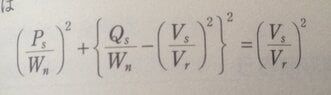- #1
aruwin
- 208
- 0
Hello.
In the attachments are the equations for power transmission circle and power reception circle. Does anyone know how they are derived?
[FONT=MathJax_Math]P[/FONT][FONT=MathJax_Math]r[/FONT]= power reception
[FONT=MathJax_Math]P[/FONT][FONT=MathJax_Math]s[/FONT]=power transmission
I think [FONT=MathJax_Math]W[/FONT][FONT=MathJax_Math]n[/FONT] is the power reference.
In the attachments are the equations for power transmission circle and power reception circle. Does anyone know how they are derived?
[FONT=MathJax_Math]P[/FONT][FONT=MathJax_Math]r[/FONT]= power reception
[FONT=MathJax_Math]P[/FONT][FONT=MathJax_Math]s[/FONT]=power transmission
I think [FONT=MathJax_Math]W[/FONT][FONT=MathJax_Math]n[/FONT] is the power reference.
Attachments
Last edited: