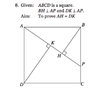
- #1
Yazan975
- 30
- 0
View attachment 8758View attachment 8759
This is where I got so far. I can't figure out how to prove AH = DK in order to prove the HL property of congruency
This is where I got so far. I can't figure out how to prove AH = DK in order to prove the HL property of congruency