- #1
Hitman6267
- 17
- 0
A block with a speaker bolted to it is connected to a spring having spring constant k= 20.0 N/m as in Figure P17.40. The total mass of the block and speaker is 5.00 kg, and the amplitude of this unit's motion is 0.500 m. (a) If the speaker emits sound waves of frequency 440 Hz, determine the highest and lowest frequencies heard by the person to the right of the speaker. (b) If the maximum sound level heard by the person is 60.0 dB when he is closest to the speaker, 1.00 m away, what is the minimum sound level heard by the observer? Assume that the speed of sound is 343 m/s.
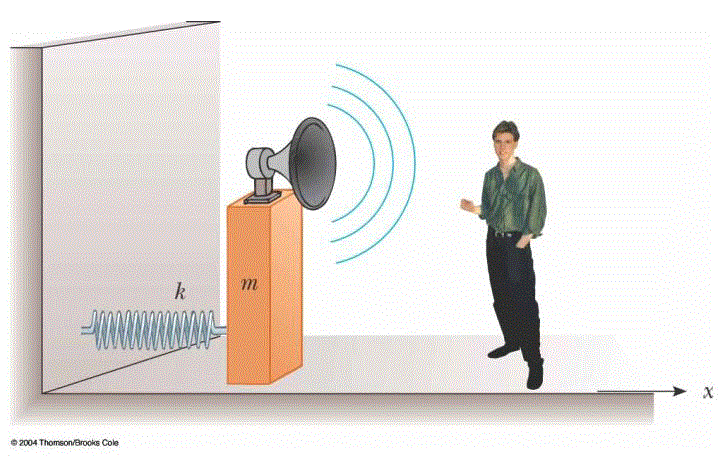
The solution
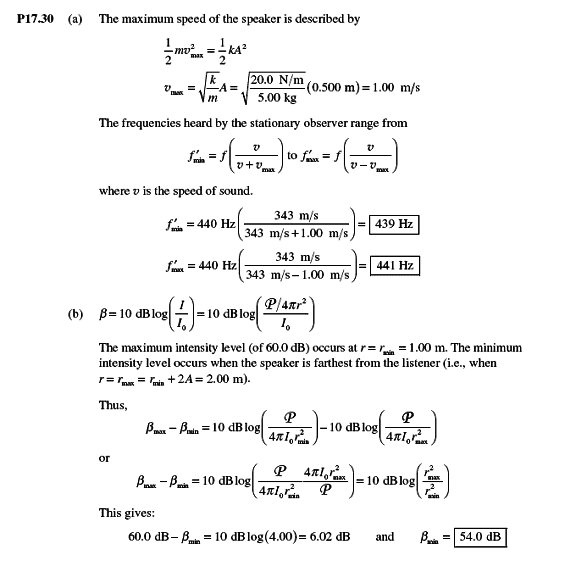
Can some one tell me what are the formulas they used in part a ? I can't find them in my book (Halliday, fundamentals of physics)
The solution
Can some one tell me what are the formulas they used in part a ? I can't find them in my book (Halliday, fundamentals of physics)