- #1
DharmaSC815
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
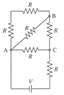
Find the net resistance in the circuit. each resistance is 3.3 kOhms. see attached
Thanks!
Homework Equations
series r=r1+r2+r3...
parallel 1/r=1/r1+1/r2...
The Attempt at a Solution
I tried taking into account the short circuit and just adding two. Also tried resistance of 2 in parallel and 4 in series.