- #1
goodOrBad
- 25
- 2
- Homework Statement
- If given G find weight Q necessary for a uniform descent of G
- Relevant Equations
- Fx=0
Fy=0
This is my attempt of solving it
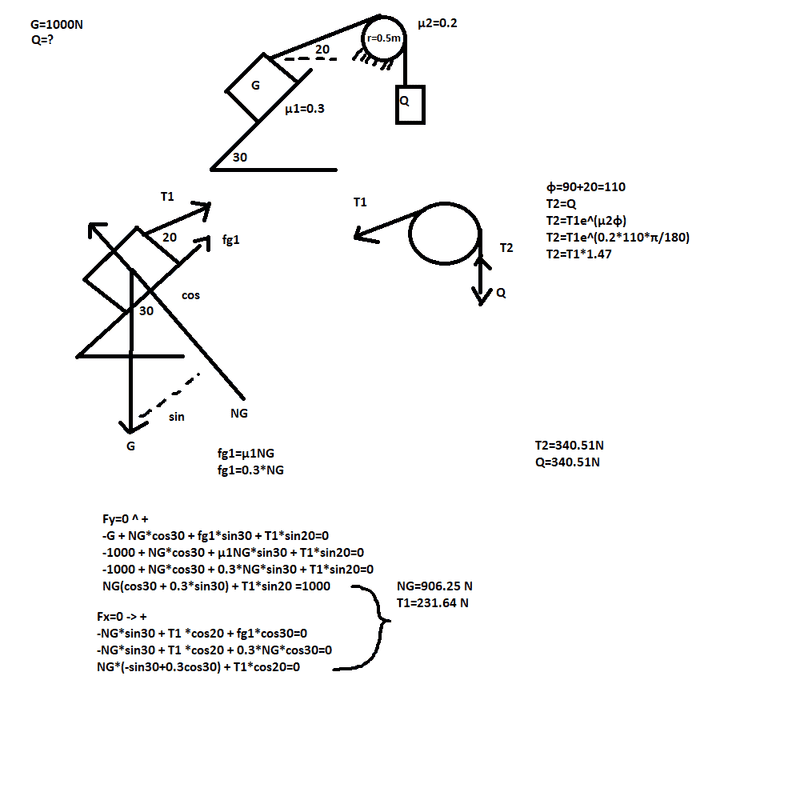
Yes.goodOrBad said:or should the angle of T1 be 50 due to the slope being 30deg and the rope 20deg so 50deg
and that means angle around the pulley is 50+90=140deg
A "block on a slope with a weight" refers to a physical system where a block or object is placed on a slope or incline and has a weight acting on it due to gravity.
The angle of the slope plays a crucial role in determining the block's movement. A steeper slope will result in a greater gravitational force acting on the block, causing it to accelerate faster and slide down the slope at a higher speed. A shallower slope will result in a smaller gravitational force and slower movement.
The friction between the block and the slope is influenced by several factors, including the roughness of the surface, the weight of the block, and the angle of the slope. A rougher surface will result in a higher frictional force, while a smoother surface will have a lower frictional force. A heavier block will also experience a greater frictional force, and a steeper slope will result in a higher frictional force due to the increased normal force.
The weight of the block has a direct impact on its acceleration down the slope. The greater the weight of the block, the greater the force of gravity acting on it, resulting in a larger acceleration. This means that a heavier block will slide down the slope at a faster rate compared to a lighter block.
The normal force is the perpendicular force exerted by the slope on the block. It counteracts the force of gravity and is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. The normal force also plays a crucial role in determining the amount of friction between the block and the slope, as it is directly proportional to the frictional force.