- #1
VHAHAHA
- 58
- 0
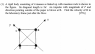
Homework Statement
The problem is shown below.
Homework Equations
Conservation of momentum? pi = pf
∫Fdt = I ?
The Attempt at a Solution
This question is really strange. I have started to do this question for many hours and I don't know how to start it.
I have tried to list out the equations like Conservation of momentum and ∫Fdt = I , but i don't know how to use this equation! It is very strange ! How to get start? I have also tried using the center of mass but the results are useless!
Any tips pleases? I have already attempted this equation! But the problem is I don't know how to get start! =(