- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
How Do You Solve Problems Using Thevenin and Norton Equivalents?
- Thread starter euphoria172
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Thevenin
In summary, the conversation involves a user asking for help on a question and receiving guidance from another user. The discussion includes different methods for solving the problem and addressing specific concerns. The conversation ends with the user expressing gratitude for the help received.
Physics news on Phys.org
- #2
tiny-tim
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 25,839
- 258
welcome to pf!
hi euphoria172! welcome to pf!
show us what you've tried, and where you're stuck, and then we'll know how to help!
hi euphoria172! welcome to pf!
show us what you've tried, and where you're stuck, and then we'll know how to help!
- #3
- #4
gneill
Mentor
- 20,989
- 2,934
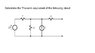
Why do feel that your Method 1 is incorrect? The results look fine  It appears that you first found the Thevenin equivalent of the voltage source and first two resistors and then applied superposition to find the final Voc. Nothing wrong with that.
It appears that you first found the Thevenin equivalent of the voltage source and first two resistors and then applied superposition to find the final Voc. Nothing wrong with that.
In your Method 2, it's not entirely clear to me what your steps were trying to accomplish. It appears that you were again trying to use superposition to find the contribution from each source, but for the voltage source you found the total current that it produces, not the portion flowing through the shorted output.
The method that you employed in the first attempt, namely working section by section through the circuit making Thevenin (or Norton) transformations can be very useful. It can allow you to combine sources easily as you go. Try it for the Norton equivalent: first convert the 25V source and 5 Ohm resistor to its Norton equivalent. What's then in parallel and can be combined? Rinse, repeat
In your Method 2, it's not entirely clear to me what your steps were trying to accomplish. It appears that you were again trying to use superposition to find the contribution from each source, but for the voltage source you found the total current that it produces, not the portion flowing through the shorted output.
The method that you employed in the first attempt, namely working section by section through the circuit making Thevenin (or Norton) transformations can be very useful. It can allow you to combine sources easily as you go. Try it for the Norton equivalent: first convert the 25V source and 5 Ohm resistor to its Norton equivalent. What's then in parallel and can be combined? Rinse, repeat
- #5
euphoria172
- 6
- 0
Thx gneill. I realize i make a mistake on a similar question that cause me to doubt this answer.
Thx again. I appreciate your help.
Thx again. I appreciate your help.
FAQ: How Do You Solve Problems Using Thevenin and Norton Equivalents?
What is the Thevenin theorem?
The Thevenin theorem states that any linear circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a voltage source in series with a resistor. This equivalent circuit is known as the Thevenin equivalent.
What is the Norton theorem?
The Norton theorem is a similar concept to the Thevenin theorem, but instead of a voltage source, it uses a current source in parallel with a resistor to represent a linear circuit.
What is the purpose of finding Thevenin and Norton equivalents?
Thevenin and Norton equivalents are useful in simplifying complex circuits and making them easier to analyze. They also allow for easier comparison and understanding of different circuits.
How do you find the Thevenin equivalent circuit?
To find the Thevenin equivalent circuit, you need to remove the load resistor from the original circuit and calculate the open-circuit voltage and the equivalent resistance seen from the load terminals.
How do you find the Norton equivalent circuit?
To find the Norton equivalent circuit, you need to remove the load resistor from the original circuit and calculate the short-circuit current and the equivalent resistance seen from the load terminals.
Similar threads
Engineering
How do I find Vth with the node voltage method?
- Replies
- 10
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 9
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 17
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 2K
Engineering
Converting to a circuit's Thevenin equivalent?
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 6K
Engineering
How to Calculate Thevenin Equivalent Circuit
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
Share: