- #1
gummybeargirl
- 22
- 0
Homework Statement
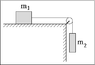
Mass m1 = 14.9 kg is on a horizontal surface. Mass m2 = 7.48 kg hangs freely on a rope which is attached to the first mass. The coefficient of static friction between m1 and the horizontal surface is μs = 0.571, while the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk = 0.105. If the system is in motion with m1 moving to the left, then what will be the magnitude of the system's acceleration? Consider the pulley to be massless and frictionless.
Homework Equations
∑F = ma
The Attempt at a Solution
For m1: T-μs*m1*g = m1*a
For m2: -T-m2*g = m2*a
Then i substitute → -m2*a-m2*g-μ*m1*g = m1*a
When i plug in my numbers i get the acceleration to be 2.59 m/s^2, which i correct if the system where moving right. I am not sure where i am going wrong or how to get the acceleration going left.