- #1
stargirl17
- 23
- 0
Homework Statement
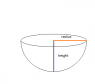
a 2.00 g ice flake is released from the edge of a hemispherical bowl whose radius is 22.0 cm. the Flake-bowl contact is frictionless. How much work is done on the flake by the gravitational force during the flake's descent to the bottom of the bowl?
Homework Equations
w=fd
The Attempt at a Solution
do i use 9.81 m/s^2 as the force?
and how do i know the distance?