Alpha2021
- 11
- 1
I am familiar with the process of calculating cross sections using tree-level Feynman diagrams. Currently, I'm keen on learning how to calculate the Feynman amplitude for a specific diagram displayed in the attached images. I'm wondering if there are any study materials available that offer a step-by-step approach to comprehending and calculating this particular process. Specifically, I'm interested in cases where x_3 and x_4 can be either scalar, fermion, or gauge boson particles.
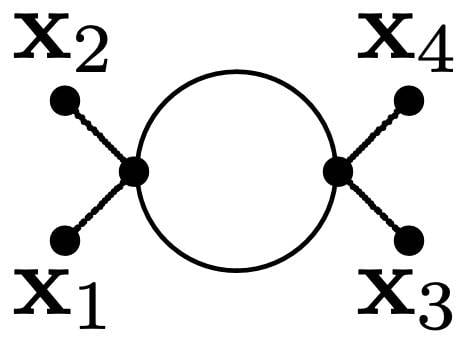
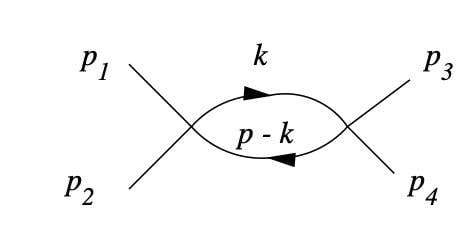
Last edited: