DumpmeAdrenaline
- 80
- 2
- Homework Statement
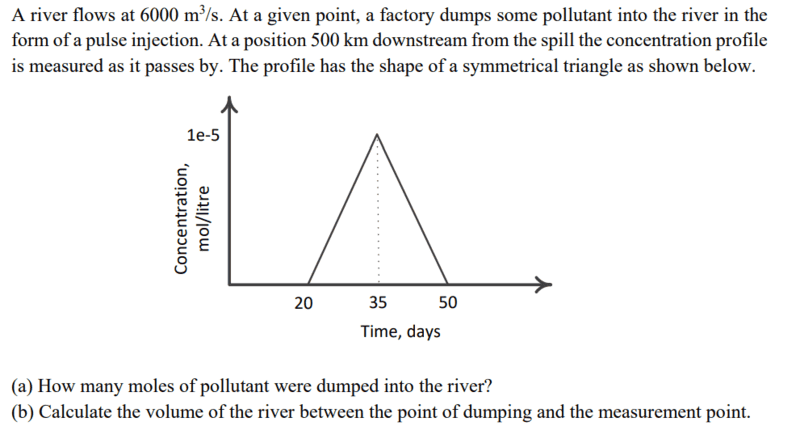
- A river flows at 6000 m^3/s. At a given point, a factory dumps some pollutant into the river in the form of a pulse injection. At a position 500 km downstream from the spill the concentration profile is measured as it passes by. The profile has the shape of a symmetrical triangle as shown below. (a) How many moles of pollutant were dumped into the river? (b) Calculate the volume of the river between the point of dumping and the measurement point.
Expert Answer
- Relevant Equations
- $$ E(t)=\frac{C(t)}{\int_0^{\infty} C(t)dt}
$$ \tao=\int_0^{\infty} tE(t)dt $$
$$ \tao=\frac{Q}{V}
The number of moles dumped into the river from the concentration at the measuring point by summing the amount of $$ \Delta{N} $$ between 20 and 50.
$$ \int_{20}^{50} Q_{river}C(t)dt=777,60,000 moles $$
The center of the pulse is the mean residence time.
$$ \frac{V}{Q}=35 $$
$$ Q=6000 m^3/s=5.184*10^8 \frac{m^3}{day}$$
$$ V=35(days)* 5.184*10^8 \frac{m^3}{day}=1.8144 V $$
$$ \int_{20}^{50} Q_{river}C(t)dt=777,60,000 moles $$
The center of the pulse is the mean residence time.
$$ \frac{V}{Q}=35 $$
$$ Q=6000 m^3/s=5.184*10^8 \frac{m^3}{day}$$
$$ V=35(days)* 5.184*10^8 \frac{m^3}{day}=1.8144 V $$