- #1
iknowles
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
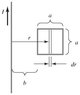
Determine the emf induced in the square loop in the figure if the loop stays at rest and the current in the straight wire is given by I(t) = (15.0 A)sin(2500t) where t is in seconds. The distance a is 12.0 cm, and b is 15.0 cm.
Homework Equations
In the question prior to this one in the homework, emf=(uIv(a^2))/(2pi(a+b)b)
The Attempt at a Solution
I initially attempted to just substitute the equation for I into the emf equation but that hasn't worked. I'm clueless on how to proceed.
Please help! Thank you!