chwala
Gold Member
- 2,827
- 415
- Homework Statement
- see attached
- Relevant Equations
- Integration -Hyperbolic Functions
Just went through this...steps pretty clear. I refreshed on Riemann integrals { sum of rectangles approximate area under curves}. My question is on the highlighted part in Red. The approximation of area under curve may be smaller or larger than the actual value. Thus the inequality may be ##<## or ##>##. Correct?
In the case of this question they chose ##>##. My point is they could have as well chosen to use ##<## with no implications.
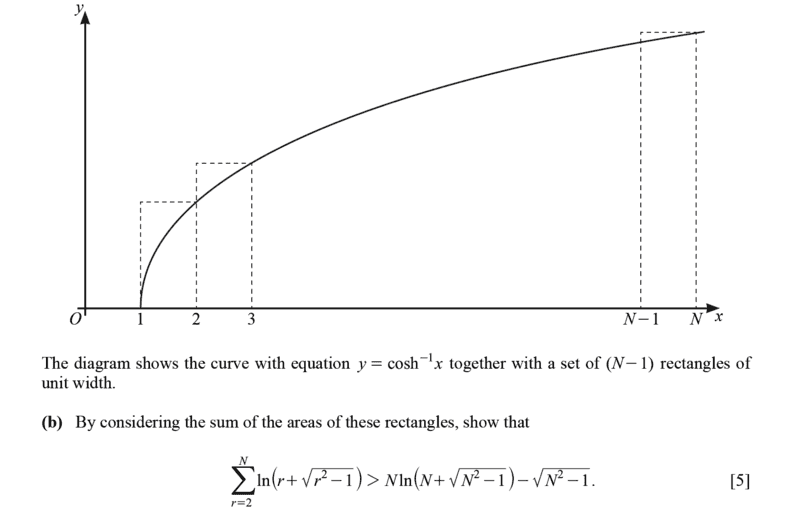
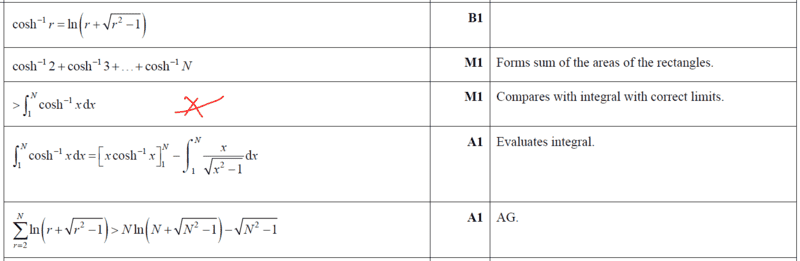
My general comments on the ms approach is as follows,
##\cosh^{-1} r = \ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} )## stems from one understanding the following steps
Let ##y = \cosh^{-1} x##
then
##x = \cosh y = \dfrac {e^y + e^{-y}}{2}##
##x= \dfrac{e^y + e^{-y}}{2}##
##2xe^y = e^{2y}+1##
...
##⇒ e^y = x ± \ln (x + \sqrt {x^2 -1} )##
##y = x ± \ln (x + \sqrt {x^2 -1} )##
They also used integration by parts noting that
##u = \cosh^{-1} x##
using
## \cosh^2 y - \sinh^2y = 1## and letting ## y =\cosh^{-1} x## then ##x = \cosh y##
##\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{1}{\sinh y}##
##\sinh y = \sqrt{\cosh^2y -1}##
##\dfrac{dy}{dx}= \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x^2-1)}}##
and lastly,
##\ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} ) > [x \ln r + \sqrt {r^2-1}]_1^N - [\sqrt {x^2-1}]_1^N##
##\ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} ) > N \ln N +\sqrt {N^2-1} -0-\sqrt {N^2-1}+0##
##\ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} ) > N \ln N +\sqrt {N^2-1}-\sqrt {N^2-1}+0##
In the case of this question they chose ##>##. My point is they could have as well chosen to use ##<## with no implications.
My general comments on the ms approach is as follows,
##\cosh^{-1} r = \ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} )## stems from one understanding the following steps
Let ##y = \cosh^{-1} x##
then
##x = \cosh y = \dfrac {e^y + e^{-y}}{2}##
##x= \dfrac{e^y + e^{-y}}{2}##
##2xe^y = e^{2y}+1##
...
##⇒ e^y = x ± \ln (x + \sqrt {x^2 -1} )##
##y = x ± \ln (x + \sqrt {x^2 -1} )##
They also used integration by parts noting that
##u = \cosh^{-1} x##
using
## \cosh^2 y - \sinh^2y = 1## and letting ## y =\cosh^{-1} x## then ##x = \cosh y##
##\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{1}{\sinh y}##
##\sinh y = \sqrt{\cosh^2y -1}##
##\dfrac{dy}{dx}= \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x^2-1)}}##
and lastly,
##\ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} ) > [x \ln r + \sqrt {r^2-1}]_1^N - [\sqrt {x^2-1}]_1^N##
##\ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} ) > N \ln N +\sqrt {N^2-1} -0-\sqrt {N^2-1}+0##
##\ln (r + \sqrt {r^2 -1} ) > N \ln N +\sqrt {N^2-1}-\sqrt {N^2-1}+0##
Last edited: