Sonderval
- 234
- 11
- TL;DR Summary
- A photon hits a beam splitter, then a non-linear crystal on both ways, the Signal photons then meet at a second beam splitter like in an MZI. Can there be interference?
Consider the following experiment:
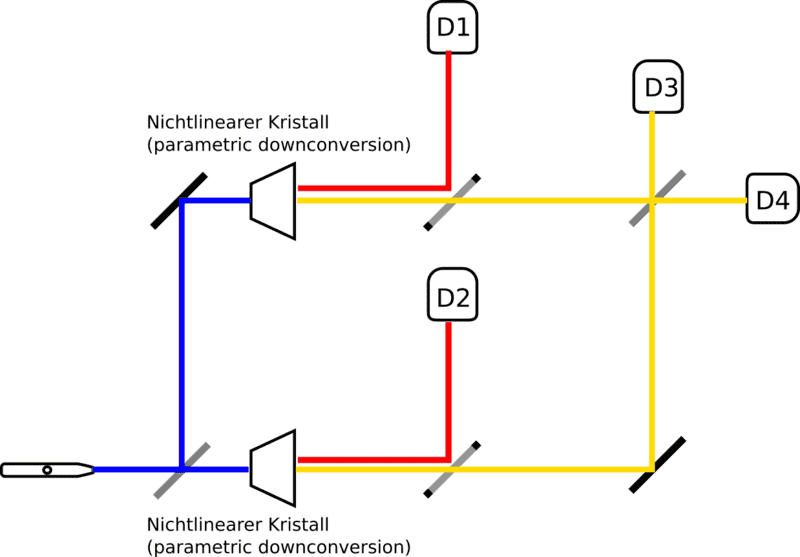
A photon hits a beam splitter, then a non-linear crystal (nichtlinearer Kristall - sorry, prepared the image in German) on each path that does parametric down conversion, splitting the photon into a signal and an idler.
The idlers proceed to two detectors (D1 and D2), the signals meet at a beam splitter.
Can there be interference at the second beam splitter so that only D3 is reached and D4 is not as in a standard Mach-Zehnder interferometer?
Does the situation change if the distance to D1 and D2 is so large that they are reached only after the signals meet at the beam splitter?
This experiment is inspired by
Lemos, Gabriela B., et al. “Quantum Imaging with Undetected Photons.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1401.4318 (2014).
In that paper, the two idlers are arranged so that they end up on the same path and are indistinguishable, so there interference is possible.
A photon hits a beam splitter, then a non-linear crystal (nichtlinearer Kristall - sorry, prepared the image in German) on each path that does parametric down conversion, splitting the photon into a signal and an idler.
The idlers proceed to two detectors (D1 and D2), the signals meet at a beam splitter.
Can there be interference at the second beam splitter so that only D3 is reached and D4 is not as in a standard Mach-Zehnder interferometer?
Does the situation change if the distance to D1 and D2 is so large that they are reached only after the signals meet at the beam splitter?
This experiment is inspired by
Lemos, Gabriela B., et al. “Quantum Imaging with Undetected Photons.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1401.4318 (2014).
In that paper, the two idlers are arranged so that they end up on the same path and are indistinguishable, so there interference is possible.