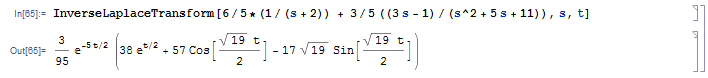Dustinsfl
- 2,217
- 5
I can't seem to part of an inverse Laplace transform correct.
\begin{align*}
f(t) &= \frac{6}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}\bigg\{\frac{1}{s + 2}\bigg\} +
\frac{3}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}\bigg\{\frac{3s - 1}
{s^2 + 5s + 11}\bigg\}\\
&= \frac{6}{5}e^{-2t} + \frac{9}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{s}{\big(s + \frac{5}{2}\big)^2 + \frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\}
- \frac{6}{5\sqrt{19}}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}}
{\big(s + \frac{5}{2}\big)^2 + \frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\}\\
&= \frac{6}{5}e^{-2t} + \frac{9}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{s}{s^2\big|_{s\to s + \frac{5}{2}} +
\frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\} - \frac{6}{5\sqrt{19}}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}}
{s^2\big|_{s\to s + \frac{5}{2}} + \frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\}\\
&= \frac{6}{5}e^{-2t} + \frac{9}{5}e^{-5/2t}
\cos\bigg(\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}t\bigg) - \frac{6}{5\sqrt{19}}
e^{-5/2t}\sin\bigg(\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}t\bigg)
\end{align*}
When I check this with Mathematica, I should have \(\frac{17}{5\sqrt{19}}e^{-5/2t}\sin\left(\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}t\right)\).
What am I doing wrong?
\begin{align*}
f(t) &= \frac{6}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}\bigg\{\frac{1}{s + 2}\bigg\} +
\frac{3}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}\bigg\{\frac{3s - 1}
{s^2 + 5s + 11}\bigg\}\\
&= \frac{6}{5}e^{-2t} + \frac{9}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{s}{\big(s + \frac{5}{2}\big)^2 + \frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\}
- \frac{6}{5\sqrt{19}}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}}
{\big(s + \frac{5}{2}\big)^2 + \frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\}\\
&= \frac{6}{5}e^{-2t} + \frac{9}{5}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{s}{s^2\big|_{s\to s + \frac{5}{2}} +
\frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\} - \frac{6}{5\sqrt{19}}\mathcal{L}^{-1}
\Bigg\{\frac{\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}}
{s^2\big|_{s\to s + \frac{5}{2}} + \frac{19}{4}}\Bigg\}\\
&= \frac{6}{5}e^{-2t} + \frac{9}{5}e^{-5/2t}
\cos\bigg(\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}t\bigg) - \frac{6}{5\sqrt{19}}
e^{-5/2t}\sin\bigg(\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}t\bigg)
\end{align*}
When I check this with Mathematica, I should have \(\frac{17}{5\sqrt{19}}e^{-5/2t}\sin\left(\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}t\right)\).
What am I doing wrong?