highschoolstudent454
- 5
- 0
Is this wrong?
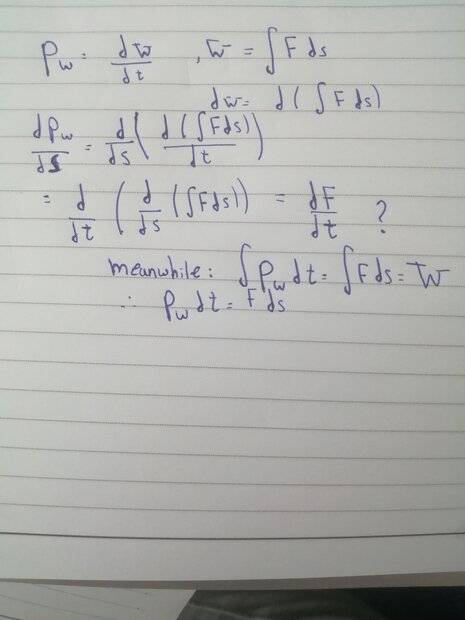
For a varying force applied at constant speed, yes.highschoolstudent454 said:Is the time derivate of force equal to the position derivative power?