- #1
stackprogramer
- 10
- 0
wein law talk in temperature upper 0 kelvin the mass have radiate that lenghth wave is λ=b/T
my question is this rule is true for all elements all products and all condition!
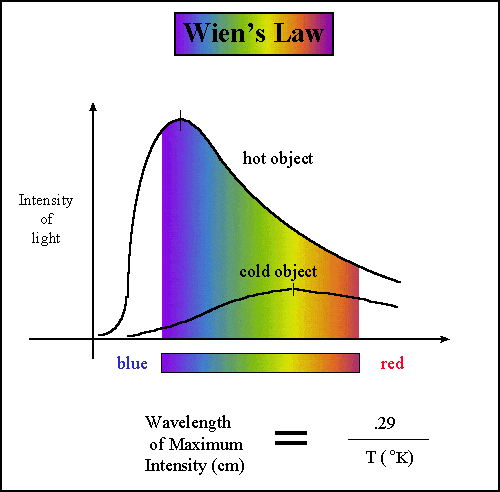
my question is this rule is true for all elements all products and all condition!