- #1
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Kinetics of Masses on an Inclined Plane: Explaining Different Movements
- Thread starter darkmagic
- Start date
-
- Tags
- Kinetics
In summary, the pulley moves only half the distance of the string, causing the 300lb block to move only half the distance of the 200lb block. This also results in the acceleration and velocity being halved. The direction of movement for the blocks can be determined by writing F = ma equations for each mass and using a linear equation to connect the heights of the masses.
Physics news on Phys.org
- #2
tiny-tim
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 25,839
- 258
Hi darkmagic! 
velocity = dx/dt and acceleration = d2x/dt2, so if you halve x, you halve velocity and acceleration also.
(and of course x is halved because the pulley moves only half as far as the string)
velocity = dx/dt and acceleration = d2x/dt2, so if you halve x, you halve velocity and acceleration also.
(and of course x is halved because the pulley moves only half as far as the string)
- #3
darkmagic
- 164
- 0
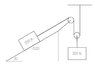
how can you know that the pulley moves only half of the string?
- #4
tiny-tim
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 25,839
- 258
When the pulley goes down 1 cm, that makes the string above it 1 cm longer on both sides, which requires 2 cm of string, so the block on the slope moves 2cm. 
- #5
- #6
tiny-tim
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 25,839
- 258
Just ask yourself, does the pulley move? if it does, how many strings are attached? (because each string will have to get longer or shorter by the same distance)
- #7
darkmagic
- 164
- 0
yes the blocks will move. my problem is in which direction will they move?
- #8
tiny-tim
Science Advisor
Homework Helper
- 25,839
- 258
To find out, write the F = ma equations for each of the three masses.
(and, if the heights of the masses are x y and z, you'll need a linear equation connecting x y and z)
(and, if the heights of the masses are x y and z, you'll need a linear equation connecting x y and z)
FAQ: Kinetics of Masses on an Inclined Plane: Explaining Different Movements
What is the definition of kinetics of rectilinear?
Kinetics of rectilinear is a branch of physics that deals with the motion of objects in a straight line.
What are the three laws of kinetics of rectilinear?
The three laws of kinetics of rectilinear are:
- Law of Inertia - An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
- Law of Acceleration - The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to its mass.
- Law of Action and Reaction - For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
What is the difference between speed and velocity in kinetics of rectilinear?
Speed is the rate at which an object covers a distance, while velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position in a specific direction. Velocity takes into account both the speed and direction of an object's motion.
What factors affect the kinetics of rectilinear?
The factors that affect the kinetics of rectilinear include mass, force, acceleration, and friction. Other factors such as air resistance, surface roughness, and temperature can also affect the motion of an object.
What is the role of calculus in understanding kinetics of rectilinear?
Calculus is used to describe the relationship between position, velocity, and acceleration in kinetics of rectilinear. It allows us to calculate the instantaneous rate of change of an object's position, velocity, and acceleration, which is essential in understanding the motion of objects in a straight line.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 22
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 540
Engineering
Control System mass spring damper
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 21
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 9
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 13
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 13
- Views
- 1K
Share: