fatpotato
- Homework Statement
- Inverting a Z-transform using Taylor series expansion
- Relevant Equations
- See embedded image in my post
Hello,
I am reading a course on signal processing involving the Z-transform, and I just read something that leaves me confused.
Let ##F(z)## be the given Z-transform of a numerical function ##f[n]## (discrete amplitudes, discrete variable), which has a positive semi-finite support and finite ROC. My textbook says that we should be able to compute the inverse Z-transform of ##F(z)##, so the ##f[n]## values, using the fact that "##f[n]## values are given by the Taylor series expansion of ##z^{-n_0} F(z^{-1})## around ##z=0##", using the following equation:
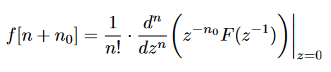
This sounds fascinating, but I don't understand! How are Z-transform and Taylor series expansion linked, and why? I only ever learned about inverting the Z-transform using tables, long division or using the inverse transform definition involving contour integral in the complex plane (which I never had the chance to use).
Any information is welcome!
I am reading a course on signal processing involving the Z-transform, and I just read something that leaves me confused.
Let ##F(z)## be the given Z-transform of a numerical function ##f[n]## (discrete amplitudes, discrete variable), which has a positive semi-finite support and finite ROC. My textbook says that we should be able to compute the inverse Z-transform of ##F(z)##, so the ##f[n]## values, using the fact that "##f[n]## values are given by the Taylor series expansion of ##z^{-n_0} F(z^{-1})## around ##z=0##", using the following equation:
This sounds fascinating, but I don't understand! How are Z-transform and Taylor series expansion linked, and why? I only ever learned about inverting the Z-transform using tables, long division or using the inverse transform definition involving contour integral in the complex plane (which I never had the chance to use).
Any information is welcome!