- #1
Thorvald
- 32
- 0
Hi.
It is relative easy to find mechanical properties for woods that can be used in building construction. But I would like to find mechanical properties for woods that can be used in bow building. That would be properties for woods such as hard rock maple, yew, bamboo, cocobolo, bolivian rosewood, bocote and such. And an additional question is: What material properties determines if a wood is good as a spring, i.e. when it is bent and released it returns to it's rest position as fast as possible.
Below is some examples of woods from a book I have.
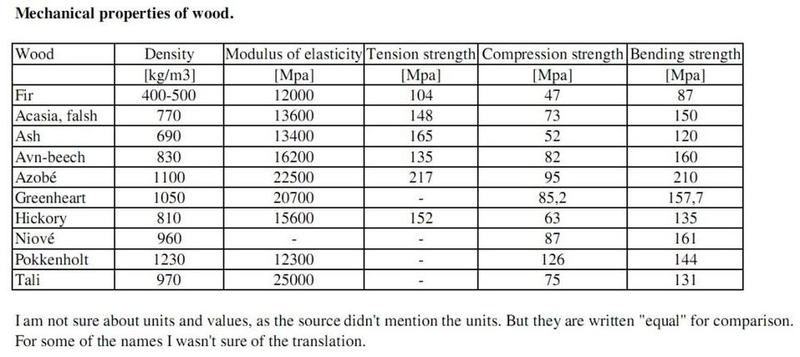
By the way - I think "Pokkenholt" is Lignum Vitae.
It is relative easy to find mechanical properties for woods that can be used in building construction. But I would like to find mechanical properties for woods that can be used in bow building. That would be properties for woods such as hard rock maple, yew, bamboo, cocobolo, bolivian rosewood, bocote and such. And an additional question is: What material properties determines if a wood is good as a spring, i.e. when it is bent and released it returns to it's rest position as fast as possible.
Below is some examples of woods from a book I have.
By the way - I think "Pokkenholt" is Lignum Vitae.