- #1
prettyinpink5
- 4
- 0
Homework Statement
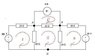
We have been doing mesh analysis of circuits, and I am just trying to work out how to do it in a larger circuit.
Homework Equations
2. Using mesh analysis work out the currents flow through each of the three meshes. From these current values calculate the voltage of node A, and node B with respect to the ground node.
3. Find equivalents of sub-circuits A-G, B-G, A-B by applying Thevinin’s theory. Then place these equivalents together and determine the voltage at Node A, and Node B. Also deduce the mesh currents from your results for the voltages at Node A an Node B and other information in the circuit.
The Attempt at a Solution
I have only gotten as far as working out the KVL's in the individual Mesh's. Not sure how to put them together in matrices