- #1
riseofphoenix
- 295
- 2
:(:(:( Please ease my aching soul by helping me with this...
I submitted this assignment online and I don't know the answers yet or however many I got wrong.

I chose 45 because I know unpolarized light becomes this after going through a polarizer:
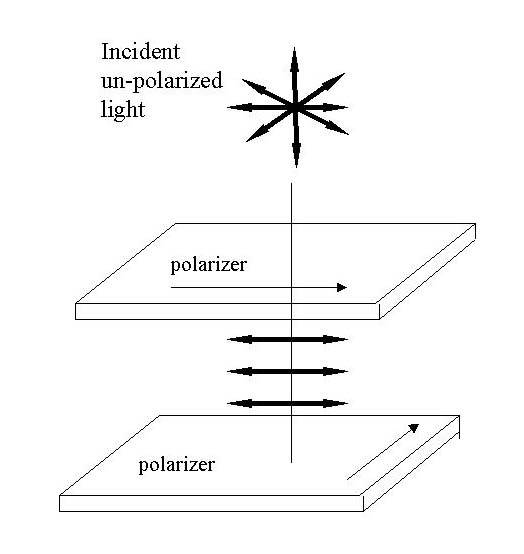
That single line is 180º, so I did 0.25 x 180º = 45º.
Is E the right answer?

I chose E…but after seeing this diagram below just now, I think I got the answer wrong and that it's supposed to be B… Is E not the answer?
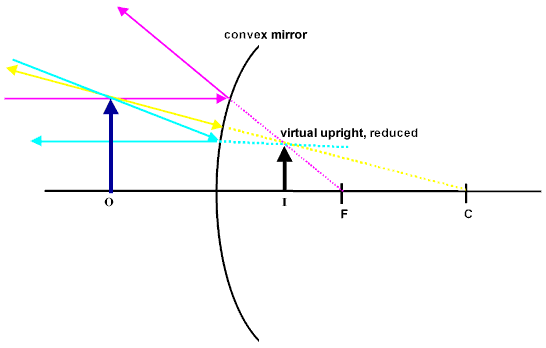

I chose D…but I don't think it's right…
I did this:
Given:
R = 10 cm
f = -R/2 (since it's convex) = -10/2 = -5
do = ?
M = +4 x (image is upright)
di = -? (image is virtual)
M = -di/do
4 = -di/do
di = -4do
1/f = 1/do + 1/di
1/(-5) = 1/do + 1/(-4do)
-0.2 = 1/do - 1/4do
-0.2 = (4/4)1/do - (1/1)1/4do
-0.2 = (4 - 1)/4do
-0.2 = 3/4do
4do = 3/(-0.2)
4do = -0.6
do = -0.6/4
do = -0.15
Is the answer C? (I chose D originally and I can't change my answer….but now that I've worked it out step by step i think the answer is C)
I submitted this assignment online and I don't know the answers yet or however many I got wrong.
I chose 45 because I know unpolarized light becomes this after going through a polarizer:
That single line is 180º, so I did 0.25 x 180º = 45º.
Is E the right answer?
I chose E…but after seeing this diagram below just now, I think I got the answer wrong and that it's supposed to be B… Is E not the answer?
I chose D…but I don't think it's right…
I did this:
Given:
R = 10 cm
f = -R/2 (since it's convex) = -10/2 = -5
do = ?
M = +4 x (image is upright)
di = -? (image is virtual)
M = -di/do
4 = -di/do
di = -4do
1/f = 1/do + 1/di
1/(-5) = 1/do + 1/(-4do)
-0.2 = 1/do - 1/4do
-0.2 = (4/4)1/do - (1/1)1/4do
-0.2 = (4 - 1)/4do
-0.2 = 3/4do
4do = 3/(-0.2)
4do = -0.6
do = -0.6/4
do = -0.15
Is the answer C? (I chose D originally and I can't change my answer….but now that I've worked it out step by step i think the answer is C)