- #1
Raazi
- 7
- 0
Hi,
I am trying to design or find a simulator for hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions which can be used in tandem with a multi-objective optimization framework such as Jmetal or etc... I am having trouble determining a generalized approach for modeling the contact angle from younge's equation for contact angle:
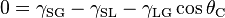
I am at a loss for how these interfacial energies might be modeled as I have very little prior knowledge of physical chemistry or material science. My aim is to design an open source simulator similar to this (https://sites.google.com/site/hydroenglish/) one where the materials, liquid, texture of the surface can be changed. If anyone can guide me towards some resources or knowledge bases which help explain the calculations used to simulate the interfacial energies shown in the equation above (without using experimental approaches) I would appreciate it a lot.
Cheers
I am trying to design or find a simulator for hydrophobic/hydrophilic interactions which can be used in tandem with a multi-objective optimization framework such as Jmetal or etc... I am having trouble determining a generalized approach for modeling the contact angle from younge's equation for contact angle:
I am at a loss for how these interfacial energies might be modeled as I have very little prior knowledge of physical chemistry or material science. My aim is to design an open source simulator similar to this (https://sites.google.com/site/hydroenglish/) one where the materials, liquid, texture of the surface can be changed. If anyone can guide me towards some resources or knowledge bases which help explain the calculations used to simulate the interfacial energies shown in the equation above (without using experimental approaches) I would appreciate it a lot.
Cheers