- #1
shivajikobardan
- 674
- 54
- Homework Statement
- desing logical and physical network design(subnetting+network architecture mainly). BOQ, Components required are also asked.
- Relevant Equations
- Subnetting is relevant concept to this.
Provide IT infrastructure details for a government school with 4 departments including ISP department which are around 500 meters apart from each other. Three departments have 5 labs each with around 24 computers in each room. ISP contains server farm with server like DNS, DHCP, E-mail, FTP and webserver and the main interet router which will be connected to the upstream provider. Propose appropriate equipment (L1,L2 and L3) and physical wires for the network design.
Solution-:
1)
D1=24*5=120
D2=120
D3=120
ISP 5 hosts
2) Components required-:
a) One main router and other routers for each department and ISP.
b) servers
c) Optical fibre to connect between 2 departments and ISPs.
d) CAT 6 cable to connect to internet in hosts.
e) Wireless access point to use wifi in laptop.
f) laptop/pcs
g) switch (why do we need switch when there is router in every step in this case? I don’t see a point of using the switch)
3) Subnetting network design, logical network design-:
Assume IP address be 192.168.0.0/23
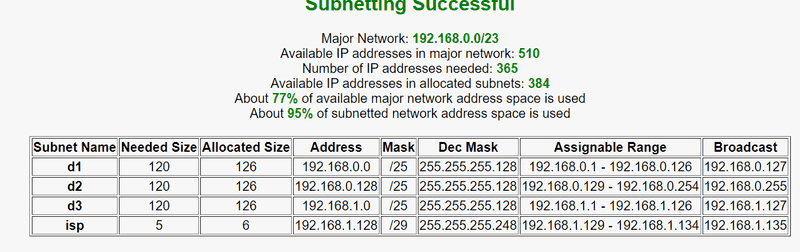
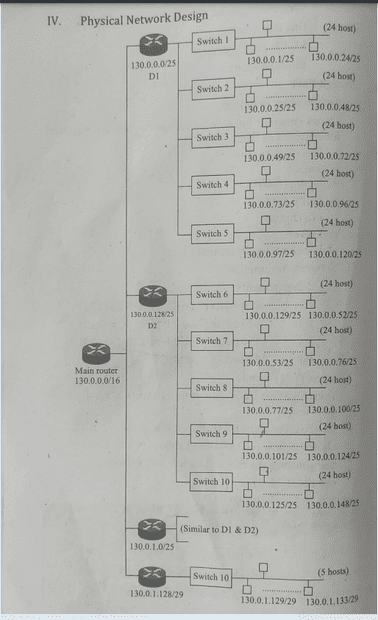
4) Physical network design(non redundant)
I tried visio and other network diagramming softwares, I could not do justice there, so I redraw the network multiple times and made this ok diagram. Hope you understand it.
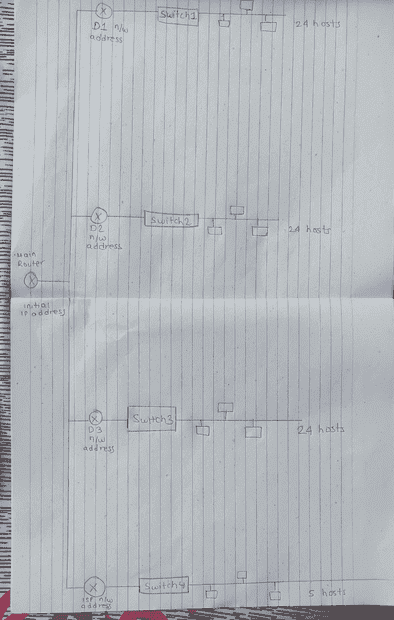
Questions-:
1) How will we make this network redundant? Will the below figure work(that solution book below?) I mean that main router isn't redundant there and it is comical that they have multiplied hosts by 5. I think we let the non redundancy at the user/access layer as per the concepts as that'd be extremely costly for users.
2) What are L1,L2 and L3 components in this? Probably it’s asking core, distribution and access layer. My guess
main router is core(I don’t think it’s as it is just the ISP),
Secondary routers and switches are distribution layer components
Hosts are access layer components.
This topic surprisingly has no similar questions answered anywhere else although the subnetting part of this is fairly common thing in many examinations. I would love to spend my whole life reading top down network design but unfortunately my course doesn’t allow me to do so.
A similar question answered here in this book-:
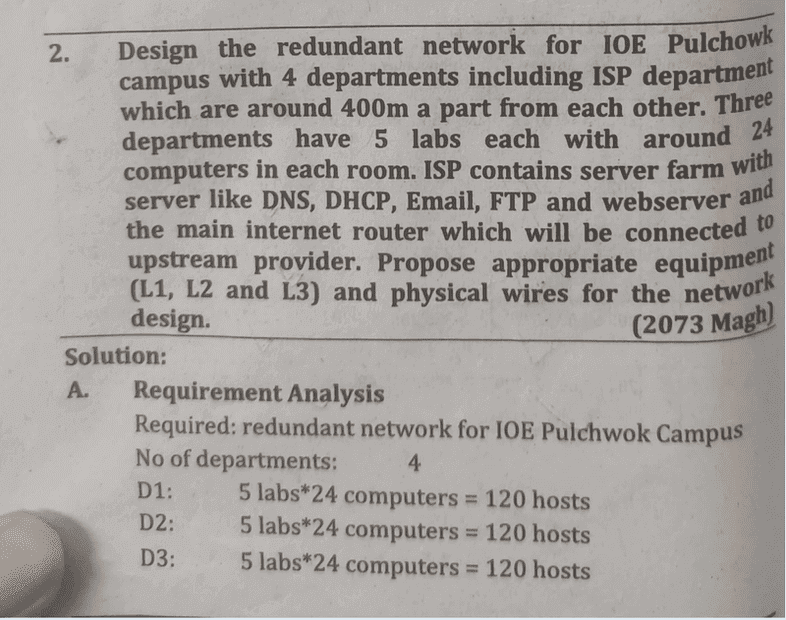


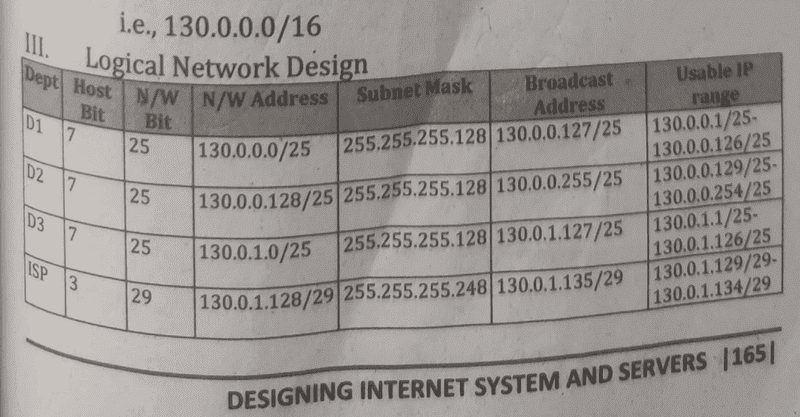
Solution-:
1)
D1=24*5=120
D2=120
D3=120
ISP 5 hosts
2) Components required-:
a) One main router and other routers for each department and ISP.
b) servers
c) Optical fibre to connect between 2 departments and ISPs.
d) CAT 6 cable to connect to internet in hosts.
e) Wireless access point to use wifi in laptop.
f) laptop/pcs
g) switch (why do we need switch when there is router in every step in this case? I don’t see a point of using the switch)
3) Subnetting network design, logical network design-:
Assume IP address be 192.168.0.0/23
4) Physical network design(non redundant)
I tried visio and other network diagramming softwares, I could not do justice there, so I redraw the network multiple times and made this ok diagram. Hope you understand it.
Questions-:
1) How will we make this network redundant? Will the below figure work(that solution book below?) I mean that main router isn't redundant there and it is comical that they have multiplied hosts by 5. I think we let the non redundancy at the user/access layer as per the concepts as that'd be extremely costly for users.
2) What are L1,L2 and L3 components in this? Probably it’s asking core, distribution and access layer. My guess
main router is core(I don’t think it’s as it is just the ISP),
Secondary routers and switches are distribution layer components
Hosts are access layer components.
This topic surprisingly has no similar questions answered anywhere else although the subnetting part of this is fairly common thing in many examinations. I would love to spend my whole life reading top down network design but unfortunately my course doesn’t allow me to do so.
A similar question answered here in this book-: