- #1
Jdo300
- 554
- 5
Hello All,
I was thinking about how electrostatic fields are used to accelerate electrons in different applications (like particle research) and I thought of a question I might run past you all. Let's say that we have an electron that is at on side of a set of charged capacitor plates. Assuming that the electron is at the negative end of the plate, it will accelerate towards the positive end, and if the positive side happens to have a hole or something in it, the charge would presumably fly out somewhere about it's merry way.
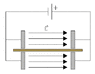
Now, what if we consider the same situation only instead of the electron sitting in open air/vacuum/whatever, it is inside of an electrical conductor (like a piece of copper wire), and this wire extends from one plate to the other, going through the hole in the positively charged plate (see my attached picture). I am wondering if the electron in the wire will still be accelerated towards the positive plate like it was in open air (i'm assuming a lot slower if at all). If this doesn't work, could someone explain to me why?
Thanks,
Jason O
P.S. if having the hole in the positive plate messes things up, then that doesn't have to be there then :-).
I was thinking about how electrostatic fields are used to accelerate electrons in different applications (like particle research) and I thought of a question I might run past you all. Let's say that we have an electron that is at on side of a set of charged capacitor plates. Assuming that the electron is at the negative end of the plate, it will accelerate towards the positive end, and if the positive side happens to have a hole or something in it, the charge would presumably fly out somewhere about it's merry way.
Now, what if we consider the same situation only instead of the electron sitting in open air/vacuum/whatever, it is inside of an electrical conductor (like a piece of copper wire), and this wire extends from one plate to the other, going through the hole in the positively charged plate (see my attached picture). I am wondering if the electron in the wire will still be accelerated towards the positive plate like it was in open air (i'm assuming a lot slower if at all). If this doesn't work, could someone explain to me why?
Thanks,
Jason O
P.S. if having the hole in the positive plate messes things up, then that doesn't have to be there then :-).
Attachments
Last edited: